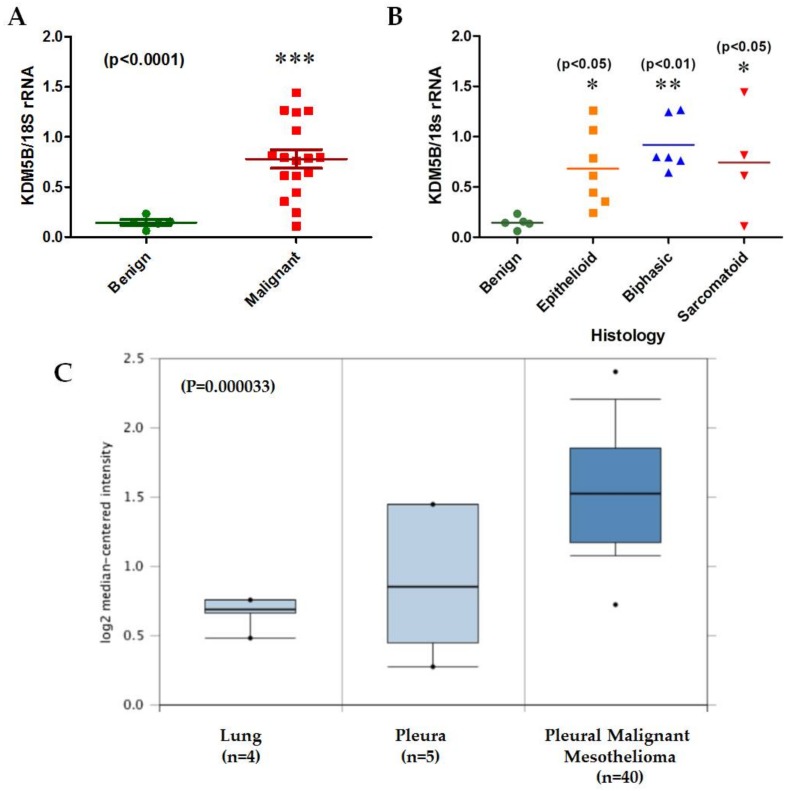
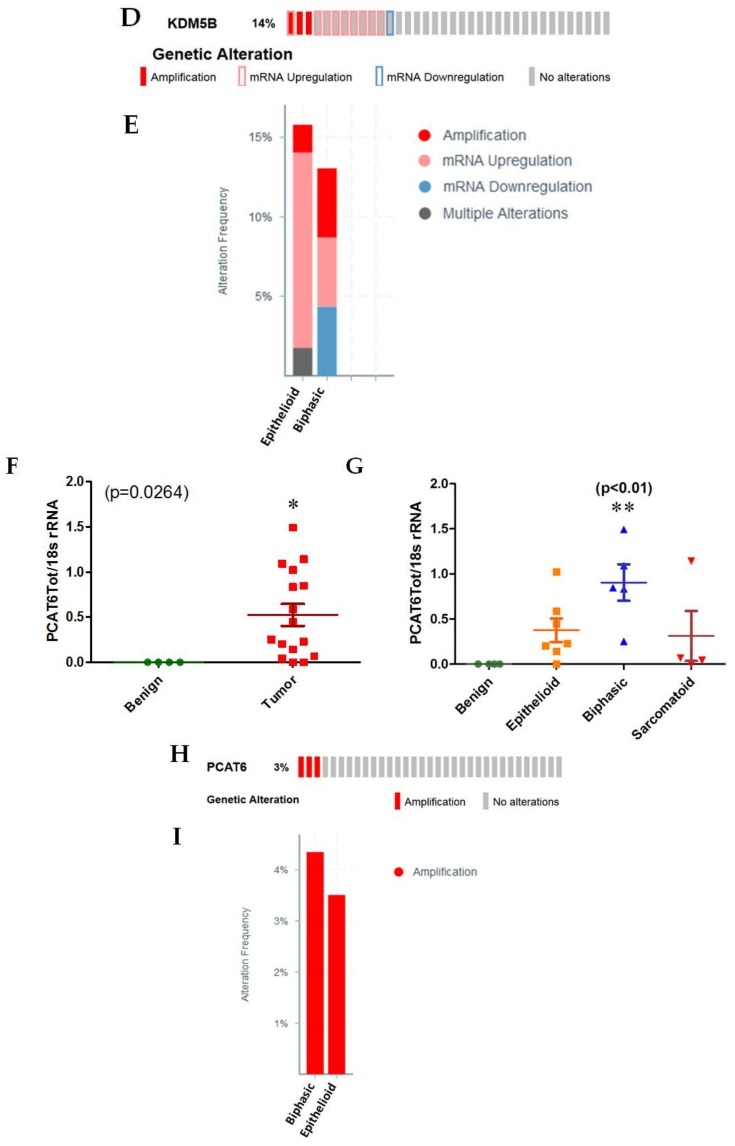
Figure 2.
An examination of KDM5B and PCAT6 expression/alterations in MPM. (A) KDM5B mRNA is significantly elevated in tumours (n = 17) compared to benign pleura (n = 5), (B) the same samples stratified by histological subtype, (C) Oncomine analysis of the Gordon mesothelioma dataset confirming significant overexpression of KDM5B, (D) in silico examination using cBioPortal reveals that 14% of samples had alterations to KDM5B, (E) when stratified by histotype, these alterations were restricted to epithelioid or biphasic subtypes, (F) total PCAT6 lncRNA is significantly elevated in tumours (n = 16(red) compared to benign pleura (n = 4—green), (G) when stratified by histological subtype (Benign = green; Epithelioid = yellow; Biphasic = blue; Sarcomatoid = red), elevated expression of total PCAT6 is significant only in the biphasic subset. Statistical significance was assessed using a Mann–Whitney t-test (* p < 0.05), or by an ANOVA using Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison Test (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001), (H) in silico examination using cBioPortal reveals that 3% of samples had amplification of PCAT6, (I) when stratified by histotype, these alterations were restricted to biphasic or epithelioid subtypes.