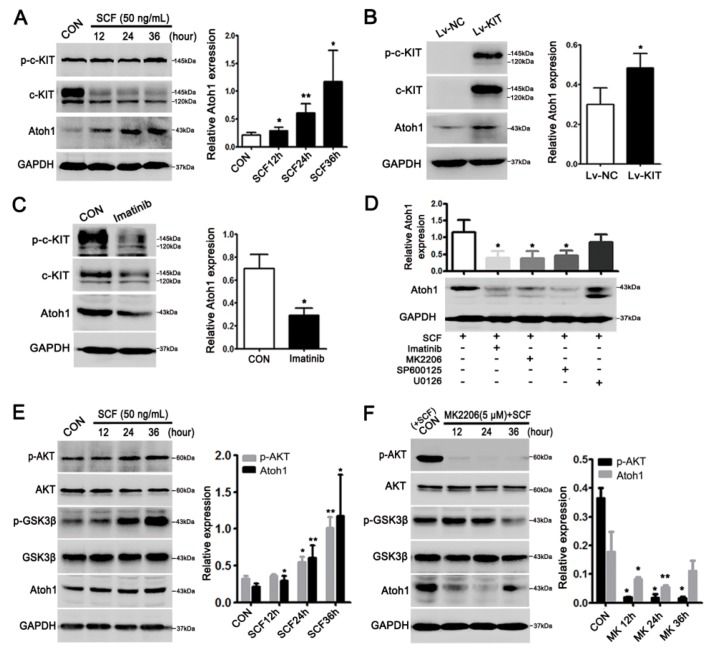
Figure 3.
Stem cell factor (SCF)/c-KIT signaling upregulated Atoh1 via Protein Kinase B (AKT) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways in LS174T cell. (A) Activation of c-KIT by exogenous recombinant human stem cell factor (rhSCF) (50 ng/mL) treatment enhanced Atoh1 expression in a time-dependent manner, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; (B) overexpression of c-KIT by lentivirus encoding c-kit clearly upregulated Atoh1 in the presence of rhSCF. Lv-NC, lentivirus-control; Lv-KIT, lentivirus-c-kit; * p < 0.05 (C) Imatinib treatment (2 μM) for 24 h to inhibit SCF/c-KIT signaling evidently attenuated Atoh1 expression, * p < 0.05; (D) CRC cells were exposed to rhSCF alone or in combination with MK2206 (AKT inhibitor), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor), or U0126 (extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) inhibitor). MK2206 or SP600125 treatment could significantly abrogate the rhSCF-induced Atoh1 expression, * p < 0.05; (E) activated c-KIT-AKT signaling pathway by rhSCF could up-regulate p-GSK3β, which, thereby, increased Atoh1. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; and (F) inhibiting AKT by MK2206 treatment significantly downregulated p-GSK3β and Atoh1. Cells with rhSCF treatment were used as control, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. All the values are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments unless otherwise stated.