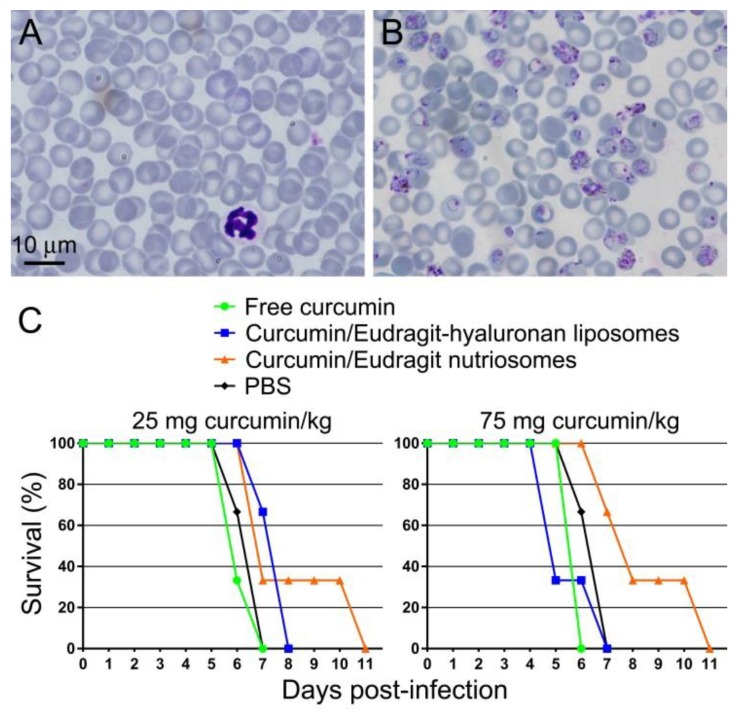
Figure 3.
In vivo antimalarial activity of orally administered curcumin. Representative microscope images of blood smears from (A) non-infected and (B) P. yoelii-infected mice. (C) Kaplan-Meier plot for the in vivo assay of the effect on P. yoelii-infected mice (n = 3 animals/sample) of free or incorporated curcumin administered orally at 25 and 75 mg·kg−1·day−1.