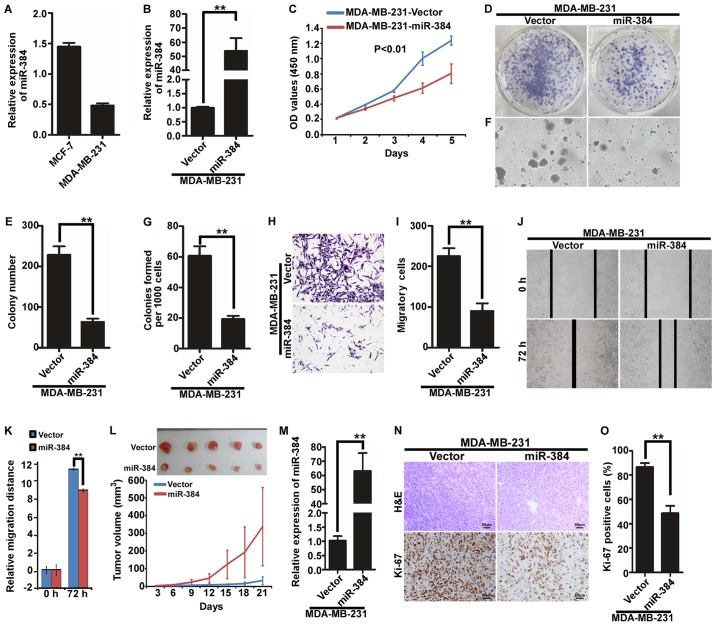
Figure 2.
Ectopic expression of miR-384 inhibits the proliferation and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro and in vivo. (A) Expression of miR-384 in breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 was detected by qCR. (B) Overexpression of miR-384 in MDA-MB-231 cells was validated by qPCR. (C) Cell growth analyzed by MTT assays. (D and E) Colony formation assay. Representative images (D) and quantification (E) of colony formation; only cell colonies containing more than 50 cells were counted. (F and G) Soft agar assay. Representative micrographs are shown (F) and only cell colonies >0.1 mm in diameter were counted (G). (H and I) Transwell migration assay. Representative images (H) and quantification (I) of migrated cells across a Transwell chamber. (J and K) Wound-healing assay. Representative images (J). Histograms represent the average migrated distances at the indicated times (K). (L) MDA-MB-231/miR-384 and MDA-MB-231/Vector cells were injected into the hind limbs of nude mice (n=5). Tumor volumes were measured on the indicated days. The tumor volume data are presented as the mean ± SD. (M) miR-384 expression in the resected mouse tumor tissues derived from MDA-MB-231/miR-384 and MDA-MB-231/Vector cells by qPCR analysis. (N and O) Histopathological analyses of xenograft tumors. The tumor sections were stained with H&E or subjected to IHC staining using an antibody against Ki-67. Error bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **P<0.01.