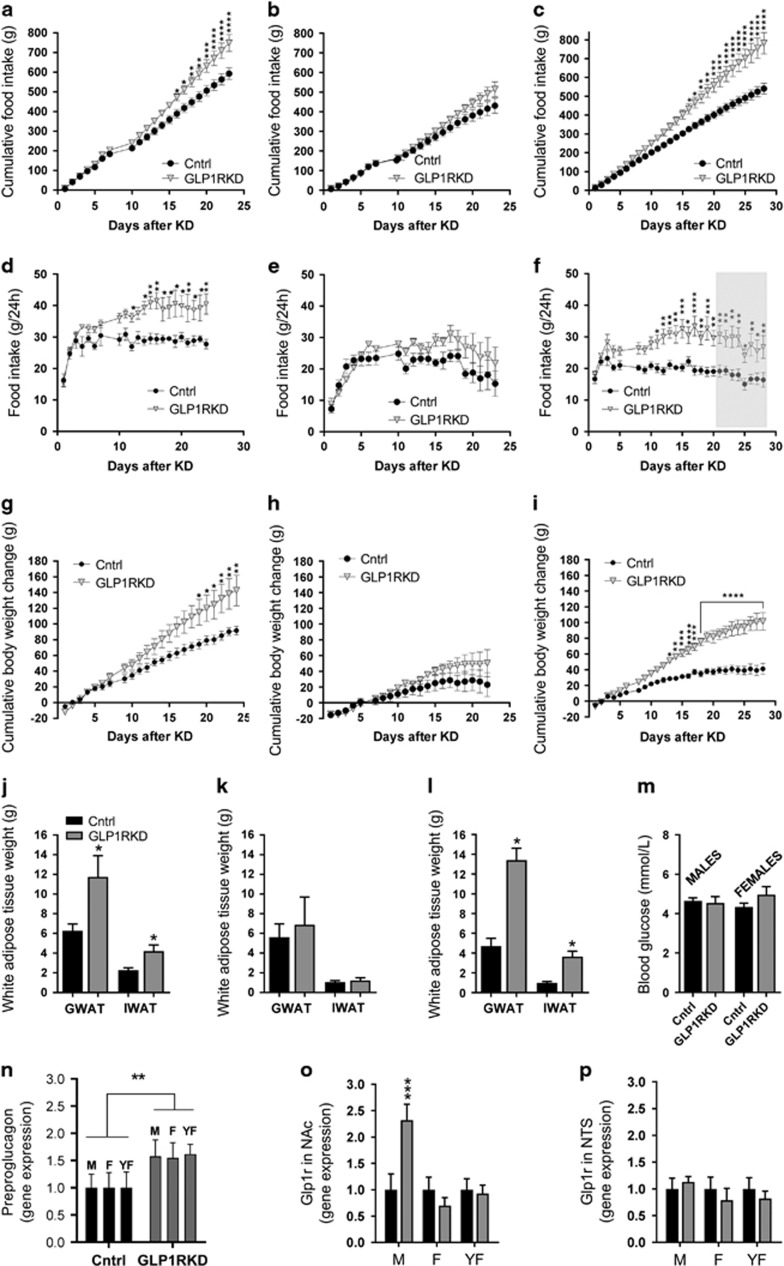
Figure 5.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) in the lateral hypothalamus (LH) are necessary for normal body weight, body fat and food intake control in males and young females but not older females. Decreased GLP-1R expression in the LH promoted a marked, chronic, hyperphagia and weight gain in male (a, d, g) but not in female (b, e, h) rats (both sexes 13 week old on injection day). In contrast to the 13-week-old females, younger females (9 week old) presented with a massive hyperphagia (c, f) and weight gain after LH GLP-1R KD (i). Likewise, male knockdown rats have double the amount of fat (j) compared with controls, while fat mass in same age females was unaffected by the treatment (k). However, the adipose tissue weight of younger females with LH GLP-1R knockdown was nearly threefold higher compared with control rats (l). Fasted blood glucose levels are not altered by the knockdown in either sex (13 week old; m). Potential compensatory adaptations of the central GLP-1 system were assessed by determining whether the GLP-1 precursor (preproglucagon) expression in the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS), or GLP-1R expression in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) or in the NTS, were altered in response to the LH GLP-1R knockdown. The expression of preproglucagon was increased in all three knockdown groups tested, thus irrespective of sex, age or weight gain response to the knockdown (n). A compensatory increase in GLP-1R expression was detected in NAc, a nucleus with dense connections to the LH, but interestingly this change was only detected in males (o). This elevation in males seemed to be area specific as GLP-1R expression in the NTS was not altered in males or any of the female groups. Thus chronic loss of LH GLP-1R, induced by an adeno-associated virus (AAV)-shRNA (short hairpin RNA) GLP-1R-mediated knockdown, not only increased food reinforcement behavior but also led to a marked hyperphagia and weight gain, at a level unparalleled to that found by blockade of any other GLP-1R population in rats or mice, despite compensatory changes detected outside of the LH. In conclusion, GLP-1R in the LH is a key component of normal body weight homeostasis and food reward control; LH emerges as one of the most critical sites for the endogenous GLP-1 effect on energy balance in males. Data are expressed as mean±s.e.m. n=10 (male rats, 5 in each treatment group); n=10 (female rats, 5 in each treatment group) for 13-week-old rats and n=16, 8 in each treatment group, for 9-week-old rats. GWAT: gonadal white adipose tissue, IWAT: inguinal (subcutaneous) white adipose tissue mass. M and F, males and females, respectively (13 week old at the time of AAV-shRNA infusion, and 17–18 week old at the time of tissue collection), YF: younger females, 9 week old at the time of infusion, and 15 at the time of tissue collection. Shaded gray area indicates a period of operant testing performed to capture a potential interaction of the knockdown with the estrous cycle. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.