Figure 4. Mismatch repair in E. coli.
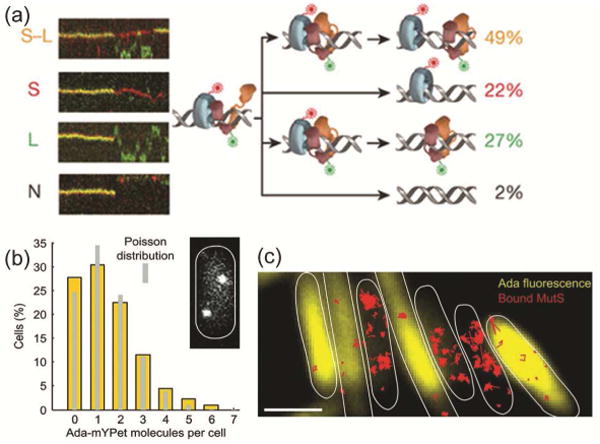
(a) Four different types of E. coli MutS/MutL complex dissociations (from top to bottom: oscillation dissociation-association, MutL dissociation, MutS dissociation, and simultaneous dissociation) observed in kymographs of E. coli MutS-AF647 (two-tone blue protein with red dye label) and MutL-Cy3 (two-tone orange protein with green dye label) diffusion in vitro on doubly-tethered mismatched DNAs. Reprinted from reference [53] by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd.: Nature 539: 583-587, Copyright 2016. (b) Single-molecule counting of Ada-mYPet in single E. coli cells measures the copy number and cell-to-cell heterogeneity of this DNA repair protein. Inset: a representative cell with two Ada-mYPet copies. (c) Cells with high Ada-mYPet expression (yellow) show fewer immobile MutS-PAmCherry molecules (red). Scale bars: 2 μm. Panels ‘b’ and ‘c’ are from Uphoff et al., Science 2016, 351:1094-1097 [54]. Reprinted by permission with permission from AAAS.
