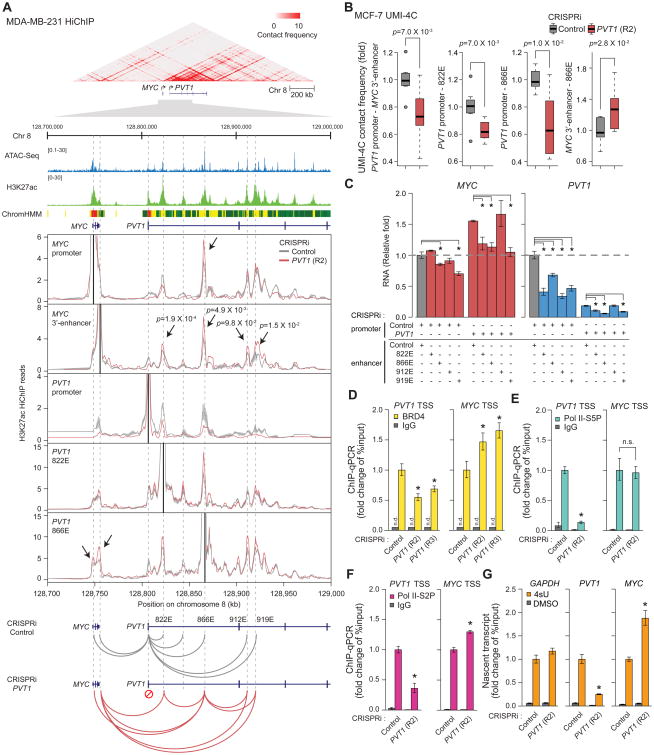
Figure 4. PVT1 promoter suppresses MYC transcription by competing for PVT1 intragenic enhancers.
A, PVT1 promoter functions as a boundary element in MDA-MB-231 cell line. Top: Heat-map representing chromatin conformation around PVT1 locus measured by H3K27ac HiChIP (n=2, biological replicates). ATAC-seq peaks, H3K27ac ChIP-seq peaks and ChromHMM diagram are shown to indicate enhancer elements. Middle: Virtual 4C plots showing H3K27ac HiChIP contact frequency at 1 kb resolution anchored at each indicated genomic position (solid black lines) with CRISPRi-Control or CRISPRi-PVT1. Bottom: Schematic diagram showing changes in chromosome interaction induced by CRISRPi-PVT1. Shaded region indicates mean ± SEM (n=2, biological replicates). p-value of each interaction between MYC 3′-enhancer and PVT1 intragenic enhancer was calculated by Fisher's exact test. B, Boxplots showing chromosome contact frequency at 5 kb resolution measured by UMI-4C in MCF-7 cell line with CRISPRi-Control or CRISPRi-PVT1 (R2). p-value was calculated by un-paired Mann-Whitney U-test (n=8). C, qRT-PCR for relative RNA level of MYC and PVT1 with dual CRISPRi targeting PVT1 promoter or intragenic enhancers in MDA-MB-231 cell line. The difference between single CRISPRi-PVT1 and dual CRISPRi-PVT1 with CRISPRi-enhancer (822E, 866E or 919E) is not significant (p>0.05). D to F, ChIP-qPCR representing relative PVT1 or MYC promoter DNA bound to BRD4 (D), Pol II-S5P (E), Pol II-S2P (F) in MDA-MB-231 cell line with CRISPRi-control or CRISPRi-PVT1. G, qRT-PCR for the relative level of 4sU-labeled nascent transcripts of PVT1 or MYC in MDA-MB-231 cell line with CRISPRi-control or CRISPRi-PVT1. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM (n=3, biological replicates). *p<0.05, using unpaired t-test compared with control (dark grey). n.s., not significant (p>0.05); n.d., not detected. See also STAR METHOD for details.