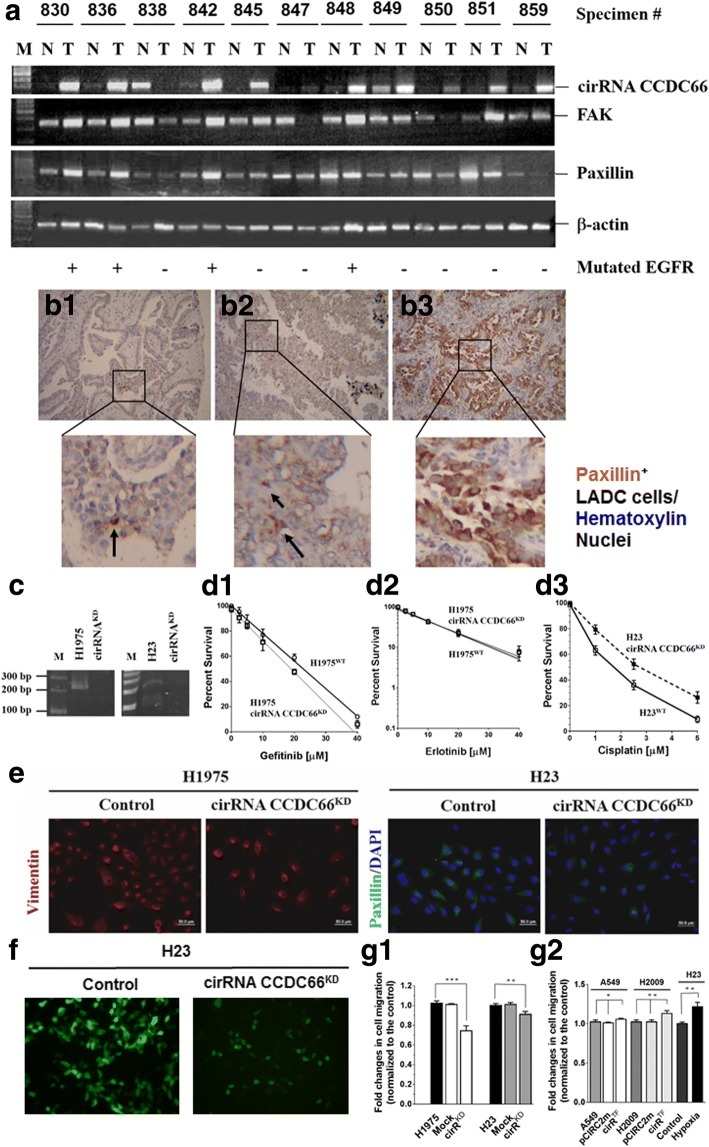
Fig. 6.
Expression of cirRNA CCDC66 correlated with that of FAK and paxillin, and knockdown of cirRNA CCDC66 reduced expression of EMT markers and invasion ability of LADC cells. a Expression of cirRNA CCDC66, FAK, and paxillin was determined by RT-PCR in 11 pairs of LADC specimens. All three tumor makers were detected in most of the tumor fractions [cirRNA CCDC66 (82%, 9/11), FAK (82%, 9/11), and paxillin (91%, 10/11)]. Paxillin was detected in tumor nests (b1–b3; b3, #836) and the neighboring areas (b2, #838) by an immunohistochemical staining. Paxillin-positive cells were in dark brown color (indicated by an arrow in b1, #859), showing EMT-like fibroblasts characteristics. c Knockdown of cirRNA CCDC66 (cirRNA CCDC66KD) expression in H1975 and H23 cells. Resistance to gefitinib (d1) or erlotinib (d2) was not markedly affected in cirRNA CCDC66KD H1975 cells (d1, d2), but clearly increased cisplatin resistance in cirRNA CCDC66KD H23 cells (d3). e Knockdown of cirRNA CCDC66 expression, however, clearly diminished expression of EMT markers (left panel, H1975 cells were stained for vimentin, red fluorescence; right panel, H23 cells were stained for paxillin, green fluorescence. Nuclei were stained with DAPI, blue fluorescence). f Silencing of cirRNA CCDC66 expression markedly reduced cell mobility across extracellular matrix protein-coated carbonate membrane. H23 cells were labeled with green fluorescence protein prior to Matrigel transmembrane assay. Cells in bottom wells of the Boyden chamber were directly detected by green fluorescence. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue fluorescence). g Effect of cirRNA CCDC66 on cell invasion ability. g1 Invasion ability of cirRNA CCDC66KD, H1975, and H23 cells decreased markedly. Statistical differences were significant (H1975 vs. Mock vs. cirRNA CCDC66KD H1975, P < 0.0001 [***], ANOVA; WT H23 vs. Mock vs. cirRNA CCDC66KD H23 cells, P = 0.0048 [**], ANOVA). [*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001]; g2 When cirRNA CCDC66 was overexpressed in A549 cells, the invasion ability increased a little (wild-type vs. pCIRC2-mCherry-transfected [pCIRC2m] vs. pCIRC2-cirRNA CCDC66-transfected A549 cells [cirRTF], P = 0.037 [*], ANOVA; wild-type vs. cirRTF A549 cells, P = 0.1054, t test). Comparing wild-type, pCIRC2m, and cirRTF H2009 cells, increment of invasion ability was significant (P = 0.0025 [**], ANOVA; H2009 vs. cirRTF H2009, P = 0.0137 [*], t test). H23 cells exposed to 24-h hypoxia were used as internal comparison parameter (P = 0.0031, t test)