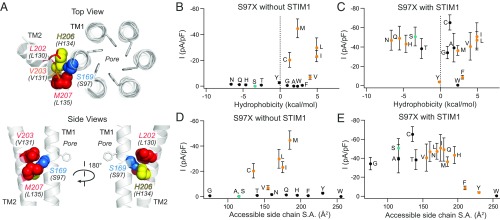
Fig. 8.
Hydrophobic substitutions at S97 evoke constitutive channel activity. (A) Top-down and side views of TMs 1 and 2 in the dOrai structure showing S169 (hOrai1 S97, blue), H206 (hOrai1 H134, yellow), and the nonpolar residues L202 (hOrai1 L130, red), V203 (hOrai1 V131, orange sticks), and M207 (hOrai1 L135, red). F99 side chains are shown as gray sticks. (B and C) The current densities of S97X mutants in the absence and presence of STIM1 coexpression are plotted against the solvation energies (in kilocalories per mole) of the substituted amino acids (47). The native Ser is depicted in teal. Substitutions that give rise to nonselective channels (Vrev < 35 mV) are shown as orange points. (D and E) Current densities of S97X mutants plotted against the accessible side-chain surface area of the introduced amino acid without and with STIM1. Mutant channels with small substitutions retain store-operated, Ca2+-selective WT behavior, whereas nonpolar or large substitutions cause the channel to become nonselective or unable to be activated by STIM1 (n = 4–11 cells; values are mean ± SEM).