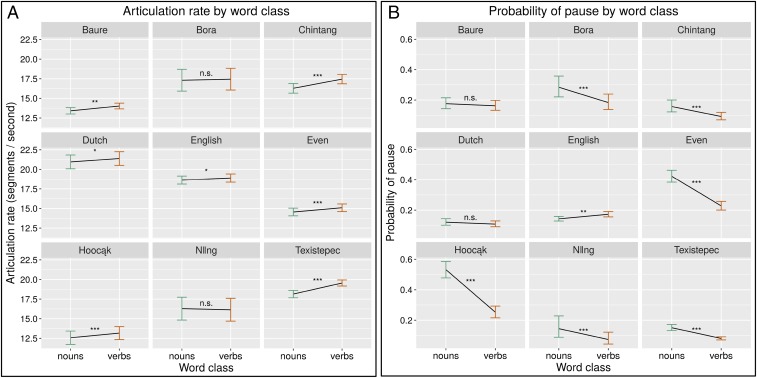
Fig. 3.
Speech rate in contexts before nouns versus verbs. The effect displays show a cross-linguistic tendency for slower articulation before nouns (A) and a higher probability of pauses before nouns (B). The effect of word class (nouns vs. verbs) is plotted according to (generalized) linear mixed-effects models, with 95% confidence intervals based on these models. Both studies are based on models that are consistent across the individual languages, controlling for word position and word length as fixed factors and including random intercepts for speaker, text, and word type. The models for articulation speed included an additional interaction between word class and position, but A shows the overall effects of word class, averaging over positions, to simplify the visual representation (Materials and Methods and SI Appendix, Supplementary Text). Levels of statistical significance are indicated as *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; and n.s. (not significant) > 0.05.