Fig. 7.
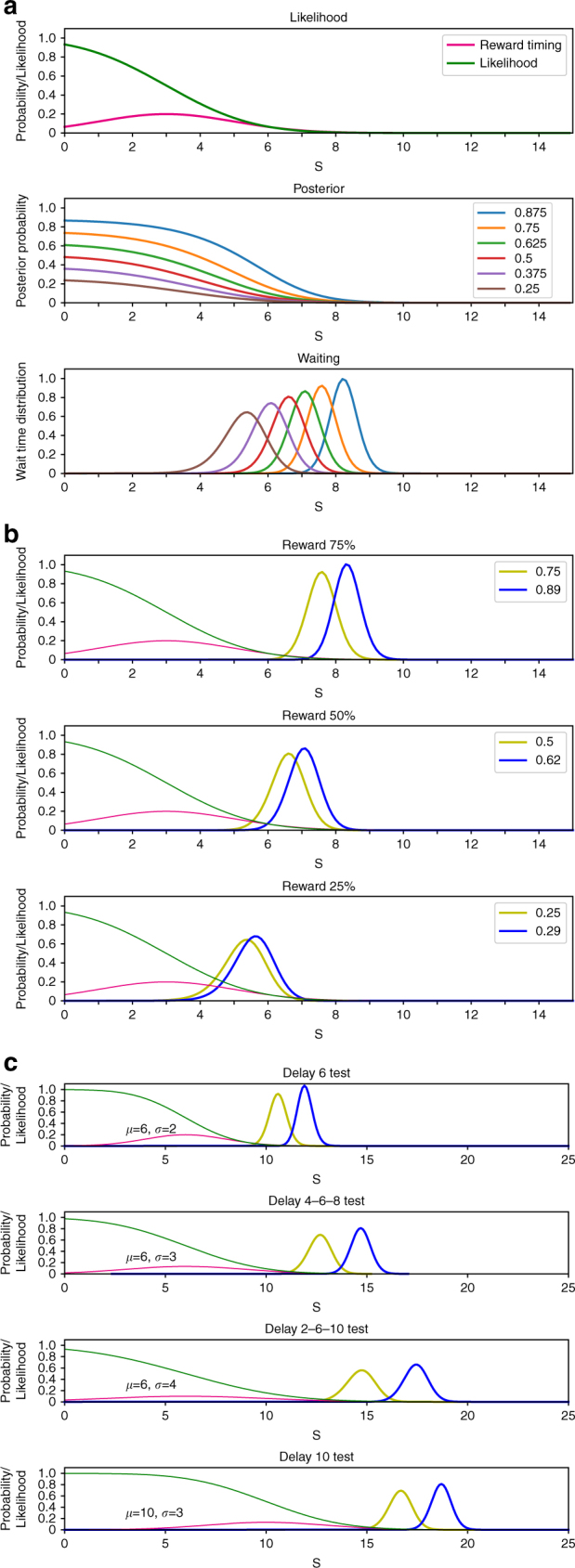
A Bayesian decision making model for waiting reproduces features of effects of reward probability and timing uncertainty on promotion of patience by serotonin. a Top panel: the model assumes that the subject has a probabilistic model of reward delivery timing (magenta line), which is assumed to be Gaussian with μ = 3 s and σ = 2 s in this example. As the time passes without reward delivery, the likelihood of a reward trial diminishes according to the cumulative density function (green line). Middle panel: the posterior probability for a reward trial goes down along with the likelihood, but persists longer if the prior probability for a reward trial is higher. Bottom panel: the timing of quitting is shifted later with a higher prior probability (Methods). b We assume that dorsal raphe serotonin neuron stimulation causes an overestimation of the prior probability when the reward probability is higher (p′ = p + p2 − p3 in this example). The yellow and blue lines show the time of quitting without and with increased prior probability, respectively. The effect of serotonin neuron stimulation is largest with a reward probability p = 0.75 (top panel; μ = 3 s and σ = 2 s). c With a larger uncertainty σ of reward timing, the waiting time distribution shifts later and the effect of serotonin neuron stimulation (increase of prior probability from 0.75 to 0.95 in this example) increases. A shift in the average reward timing (bottom panel; μ = 10 s and σ = 3 s) does not cause a large increase in waiting time with serotonin neuron stimulation
