Figure 2.
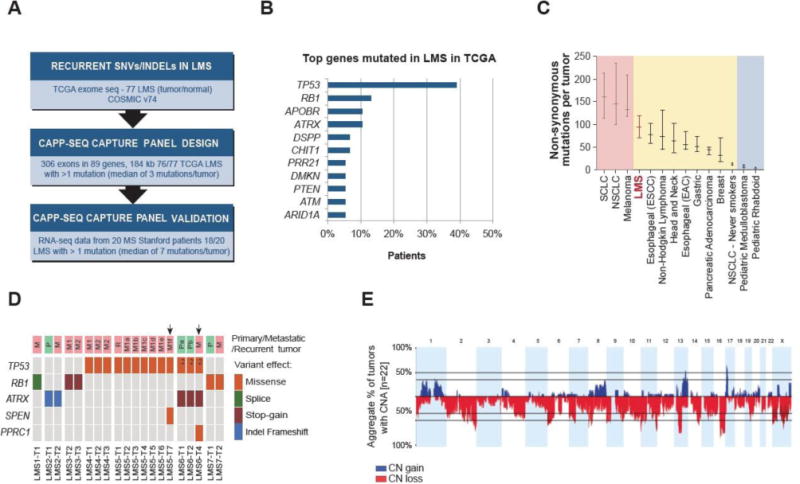
Mutational landscape of LMS and design of LMS-specific CAPP-Seq selector.
A) Design and validation of LMS-specific CAPP-Seq capture panel based on TCGA, COSMIC and Stanford sequencing data. B) The most frequently mutated genes in 77 LMS TCGA cases, according to the analysis described in the present study. C) The median number of exonic somatic mutations in LMS based on the analysis of TCGA cohort (n = 77) compared to selected types of cancer based on the studies reviewed by Vogelstein et al. (22). Horizontal bars indicate 25 and 75% quartiles. D) SNVs and indels detected by CAPP-Seq in 20 LMS tumor specimens analyzed in the present study. Arrows indicate tumor specimens with subclonal SNVs. Index 2 indicates two different somatic mutations in the same gene. M1, M2 indicate two different metastatic tumors. Pa, Pb and M1a, M1b etc. indicate different regions of the same tumor. E) Cumulative representation of copy number alterations identified by SNP array in 22 LMS tumor specimens analyzed in the present study. SCLC – small cell lung cancer; NSCLC – non-small cell lung cancer; ESCC - esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; EAC – esophageal adenocarcinoma; CN – copy number, CNA – copy number alteration.
