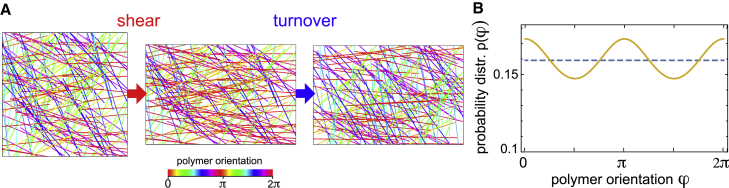
Figure 3.
Nematic alignment through shear. (A) Randomly oriented polymer rods (left panel) are reoriented by a shear deformation with . Shear deformations induce nematic alignment of biopolymers leading to a deformation-resistance proportional to active prestress (middle panel). Turnover reestablishes the original orientation distribution of polymers (right panel). The color legend indicates the orientation angle φ of polymers of different color. (B) Polymer distribution before (dashed line) and after (solid line) shear deformation with . To see this figure in color, go online.