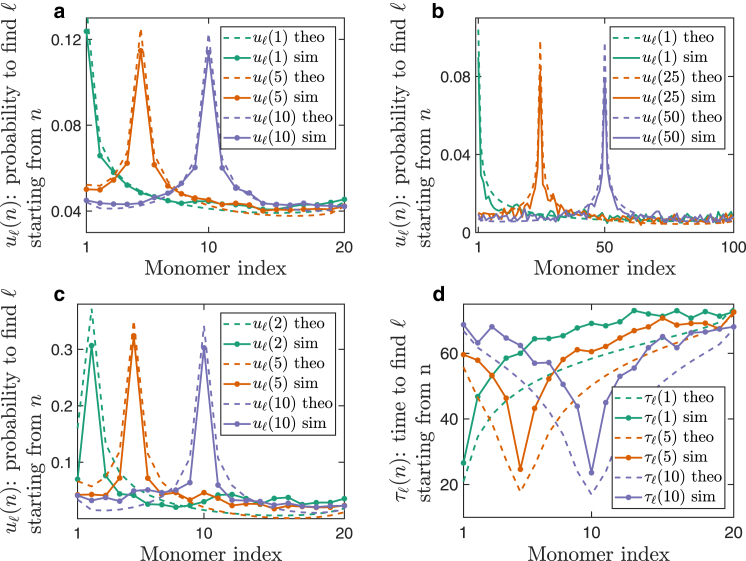
Figure 2.
Transition between monomer sites. (a) The transition probability starting from sites 1 (turquoise), 5 (orange), or 10 (purple). The polymer has 20 monomer sites (N = 20), and , , and . The solid lines are the result of Brownian simulations, whereas the dashed lines are computed using the analytical formula (Eq. 2). (b) The site transition probability when the polymer is longer (N = 100 sites). (c) The polymer is of length . It is crowded into a small domain, , and the capture radius is . (d) The mean first-transition time, , from site n to site l without interacting with any other site along the way. The full lines are the result of Brownian simulation and the dashed lines are computed using Eq. 5 with the same parameters as in (a). A single time unit is equal to, where D is the diffusion coefficient of the particle. To see this figure in color, go online.