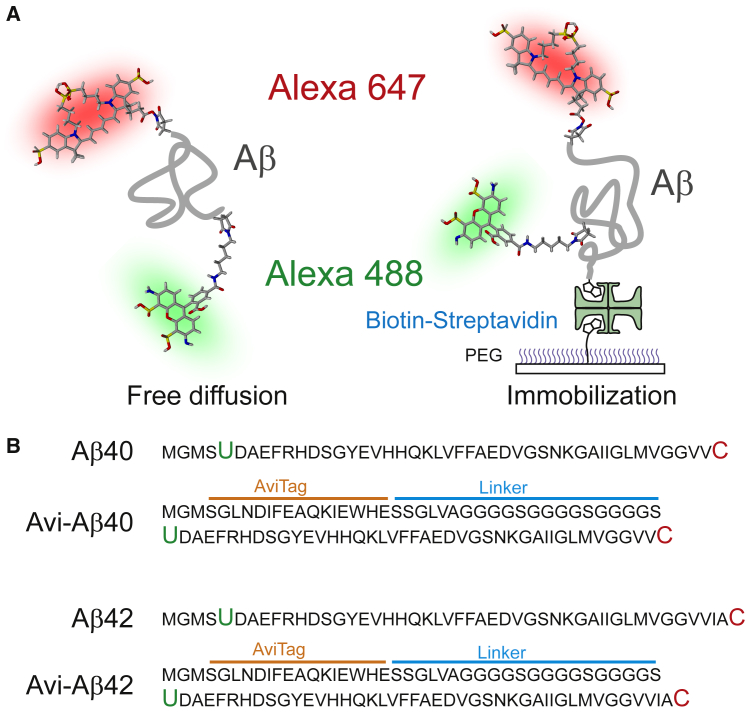
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of four amyloid β-protein constructs. (A) Aβ40 and Aβ42 (thick gray lines) are labeled with Alexa 488 (donor) and Alexa 647 (acceptor) site-specifically at the N- and C-termini, respectively. Experiments were carried out in the free-diffusion mode (left) or with molecules immobilized on a PEG-coated glass surface via a biotin-streptavidin linkage (right). (B) Amino acid sequence of the four proteins. Alexa 488 hydroxylamine is attached to the unnatural amino acid (4-acetylphenylalanine, green U) and Alexa 647 maleimide is attached to the cysteine residue (red C). For immobilization, a biotin acceptor sequence (AviTag) is added to the N-terminus of Aβ (Avi-Aβ). The glycine-rich flexible linker is inserted between AviTag and the protein to prevent potential protein-surface interactions. To see this figure in color, go online.