Figure 1.
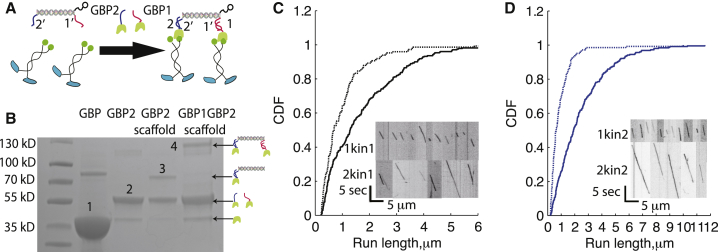
Assembly of defined multimotor assemblies using the DNA scaffold. (A) Schematic of DNA-motor assemblies. GFP binding proteins GBP1 and GBP2 were generated by covalently linking oligos 1 and 2 to the GBP through a C-terminal SNAP tag. GFP-labeled motors were then linked to the DNA scaffolds via overhanging single-stranded 1′ and 2′ appendages on the scaffold. Scaffolds were tracked by linking quantum dots to a third overhanging ssDNA on the scaffold (Fig S1A). (B) SDS-PAGE gel of DNA-protein assemblies. Electrophoresis was performed on a 4–20% polyacrylamide gel. Labeled bands are 1) unreacted GBP, 2) oligo-labeled GBP, 3) scaffold with one GBP bound, and 4) scaffold with two GBP bound. The ∼80-kDa band in the GBP lane is a minor impurity from Ni-column purification. (C) Run lengths for assemblies containing one (dashed line) or two (solid line) kinesin-1 motors in 3 mM ATP, presented as cumulative distributions. Biotin-labeled scaffolds were mixed with GBP1 and excess motors to generate one-motor assemblies, and with both GBP1 and GBP2 to generate two-motor assemblies (Fig. S1, C and D). (Inset) Kymographs of one-motor (upper) and two-motor (lower) runs for kinesin-1. Mean run lengths were 0.77 ± 0.16 and 1.62 ± 0.23 μm (mean ± 95% confidence interval, N = 150 and N = 283) for scaffolds containing one or two kinesin-1 motors, respectively. (D) Distributions and kymographs (inset) of kinesin-2 run lengths for one- (dashed line) and two- (solid line) kinesin-2 assemblies in 3 mM ATP. Mean run lengths were 0.65 ± 0.13 μm (N = 145) and 2.38 ± 0.26 μm (N = 257) for scaffolds containing one or two kinesin-2 motors, respectively. To see this figure in color, go online.