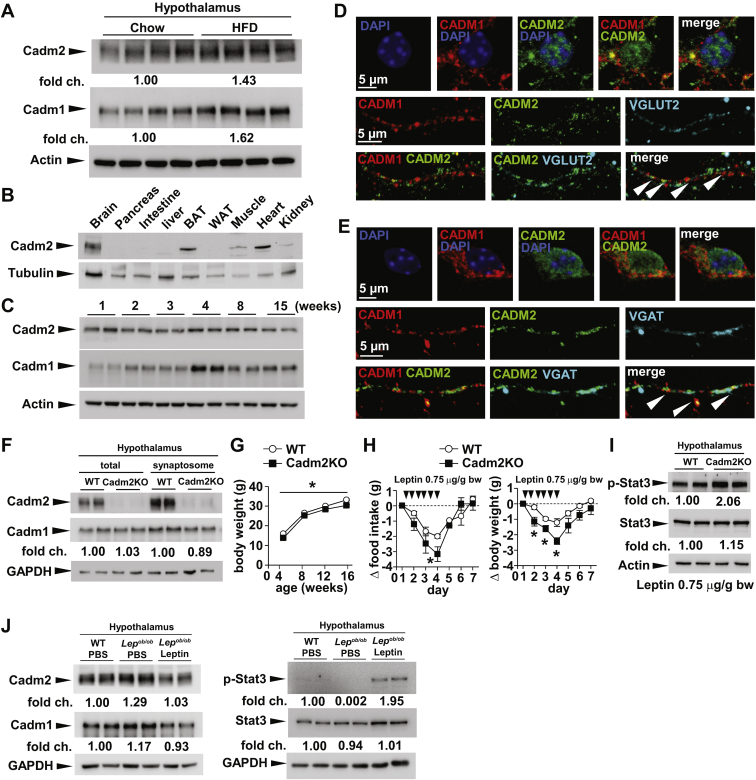
Figure 2.
Loss of Cadm2 expression results in decreased body weight and improved leptin sensitivity. A, Western blot analysis of Cadm2 and Cadm1 in total lysates from hypothalamus of wild-type mice on normal chow diet and littermate controls on high fat diet (HFD) feeding. B, Western blot analysis of Cadm2 in brain, pancreas, intestine, liver, BAT, WAT, muscle, heart in the wild-type mice. C, Western blot analysis of Cadm2 expression in wild-type brain from 1 week to 15 weeks. D, Representative confocal images of Cadm1 and Cadm2 expression in VGLUT2-positive primary hippocampal neurons. Immunostaining for Cadm1 (red), Cadm2 (green), and VGLUT2 (cyan) identify points of co-localization in dendritic branch (white arrows). E, Representative confocal images of Cadm1 and Cadm2 expression in VGAT-positive primary hippocampal neurons. Immunostaining for Cadm1 (red), Cadm2 (green), and VGAT (cyan) identify points of co-localization in dendritic branch (white arrows). F, Western blot analysis of Cadm1 and Cadm2 in total and synaptosome-enriched lysates from hypothalamus of 12-week-old Cadm2KO mice and littermate controls. G, Body weight curves of Cadm2KO mice (n = 9) and littermate controls (n = 19). H, Quantification of food intake and body weight change in 11-week old Cadm2KO (n = 4) and littermate controls (n = 4) during leptin challenge. Daily food intake and body weight was measured for 5 days prior to leptin administration for base line. I, Western blot analysis of STAT3 phosphorylation in the hypothalamus of Cadm2KO and wild-type (WT) littermates after leptin injection (0.75 μg/g body weight). p-STAT3, phosphorylated STAT3. J, Western blot analysis of Cadm1, Cadm2, and p-STAT3 in the hypothalamus of 12-week-old wild-type mice, Lepob/ob mice after 5 days PBS or leptin injection. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.