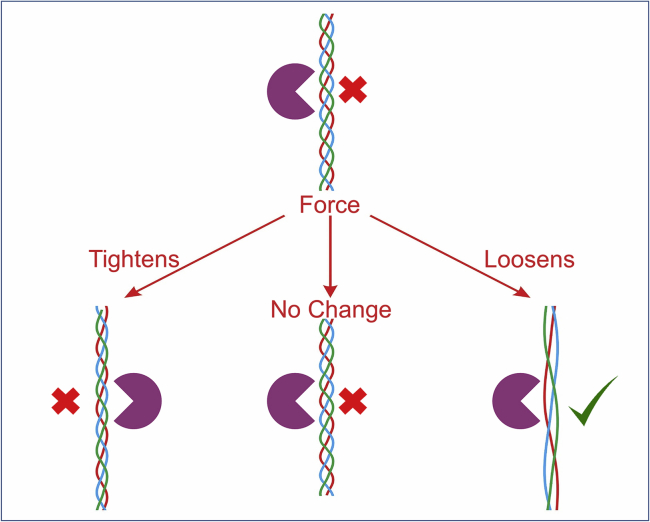
Figure 1.
Possible responses of collagen’s triple helix to applied stress. In the absence of applied force, a stable triple helix is resistant to proteolysis by trypsin (upper). If the helix tightens or remains unchanged by force (lower left and center, respectively), it remains resistant to cleavage by trypsin. Only if force induces a destabilization of the helix will proteolysis by trypsin be possible (lower right). To see this figure in color, go online.