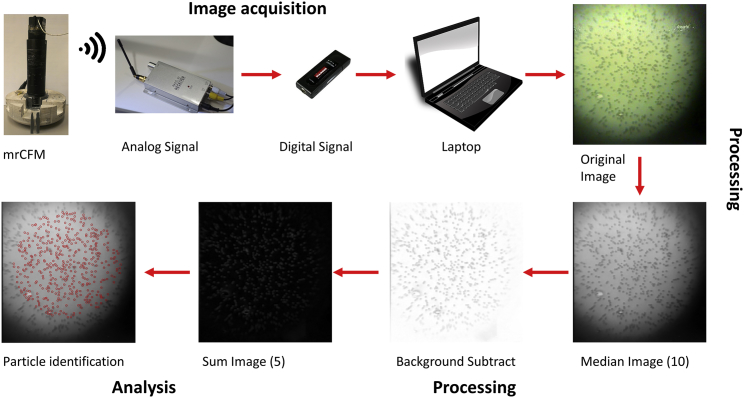
Figure 3.
Work flow for MR.CFM acquisition, processing, and analysis of bead images. Images are acquired with the wireless camera in MR.CFM, then transmitted via radio signal to the audiovisual receiver. The audiovisual receiver collects the analog signal, which is output to a USB analog-to-digital converter attached to a laptop computer, where the image stream is simultaneously visualized in real time and stored. The original output image files from MR.CFM (shown here at 9 pN of force) are processed in ImageJ to improve contrast and remove rotation-speed-dependent interference. Particles are counted using the Mosaic particle-tracking program. The resultant overlaid image visually shows that this procedure is robust and identifies beads within the defined search area. To see this figure in color, go online.