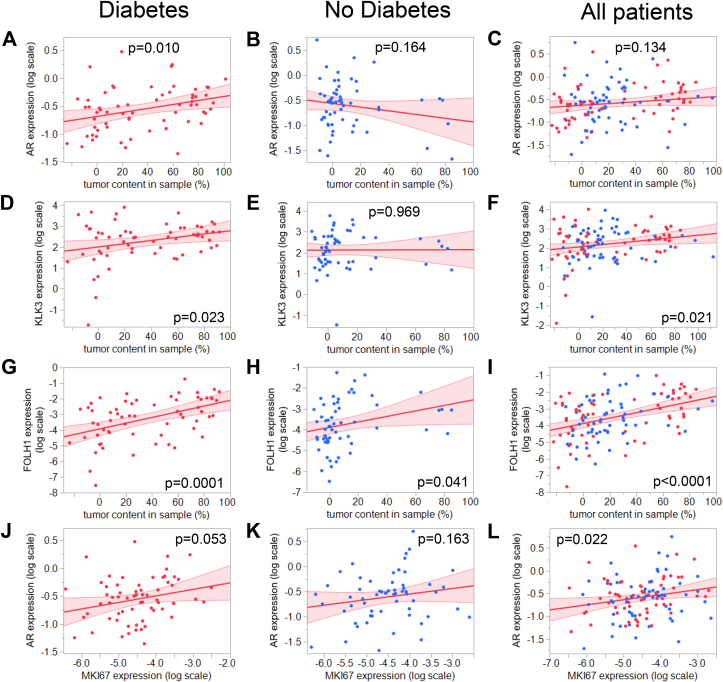
Figure 1.
Correlation between the AR mRNA expression and A–C: tumor content in sample; D–F: Correlation between KLK3 mRNA expression (encoding PSA) and tumor content in sample; G–I: Correlation between FOLH1 mRNA expression (encoding PSMA) and tumor content in sample; J–L: Correlation between AR and MKI67 mRNA expression (encoding AR and Ki-67, respectively) in diabetes (left panels, red dots), no diabetes (middle panels, blue dots) and all patients combined (right panels). Samples of men with and without type 2 diabetes who underwent a radical prostatectomy were included in the study. Tumor content was quantified by an experienced pathologist. mRNA expression of target genes was analyzed by RT-qPCR and normalized to UBC mRNA in duplicate. Red line represents fit line ±95% CI. Data were log-transformed where indicated, and associations were tested by multiple linear regression analyses with adjustment for age and BMI. Abbreviations: AR, androgen receptor; Ki-67, cell proliferation marker; PSA, prostate-specific antigen; PSMA, prostate-specific membrane antigen; UBC, ubiquitin C.