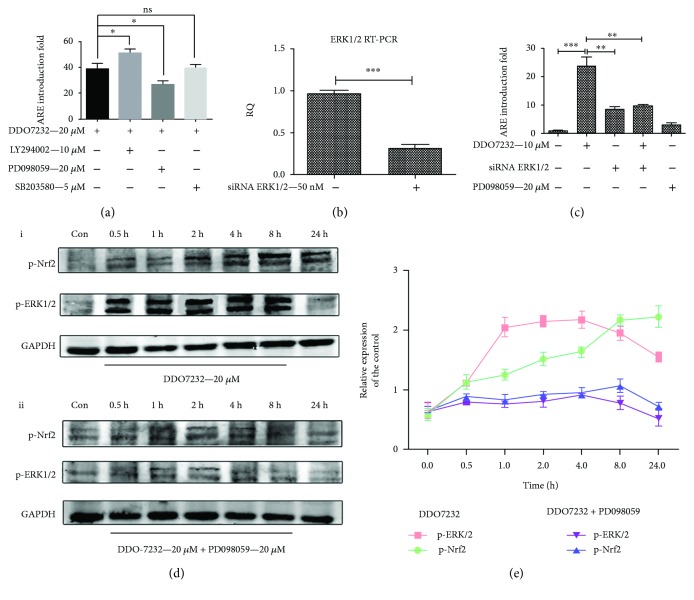
Figure 3.
DDO7232 activated Nrf2 by inducing the ERK1/2 phosphorylation. (a) The mechanism of Nrf2-ARE activation was studied using the ARE-luciferase reporter gene assay. In HepG2-ARE-C8 cells, the ARE-inducing activity was carried out with PI3K (LY294002, 10 μM), MEK1/2 (PD098059, 20 μM) or P38 (SB203580, 5 μM) inhibitors, and DDO7232 (20 μM) for 12 h and was measured using a luciferase reporter gene assay. The activity shown is relative to the DMSO control (con). (b) HepG2-ARE-C8 cells were transiently transfected with siRNA ERK1/2 (50 nM) or control siRNA. ERK1/2 mRNA transcription was evaluated by qRT-PCR. (c) ARE-inducing activity, measured by the luciferase reporter assay, changed significantly when the HepG2-ARE-C8 cells were treated with siRNA ERK1/2 (50 nM) with or without DDO7232 (10 μM). The PD098059-treated (20 μM) and DMSO blank groups were used as control groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Differences were considered statistically significant at ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001. (d) Effects of DDO7232 (20 μM) on ERK1/2 signal transduction. (i) At the indicated times after treatment with DDO7232 (20 μM), NCM460 cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and Nrf2. (ii) Phosphorylated ERK1/2 and Nrf2 expression as assayed by Western blot of NCM460 cells cotreated with DDO7232 and the MEK1/2 inhibitor, PD098059 (20 μM), blocked activation of p-ERK1/2. Con means the DMSO control group. (e) To determine the relative ratios of the p-ERK1/2 and p-Nrf2 proteins in each fraction, densitometric analysis was performed. All the data were normalized to GAPDH expression and were expressed as the mean ± SD of three individual experiments. The data were analyzed using ImageJ 1.44p. Differences were statistically significant at ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001.