Figure 3. CCG-1423 attenuates expression of several actin-binding proteins, suppresses membrane protrusion and motility of HmVEC.
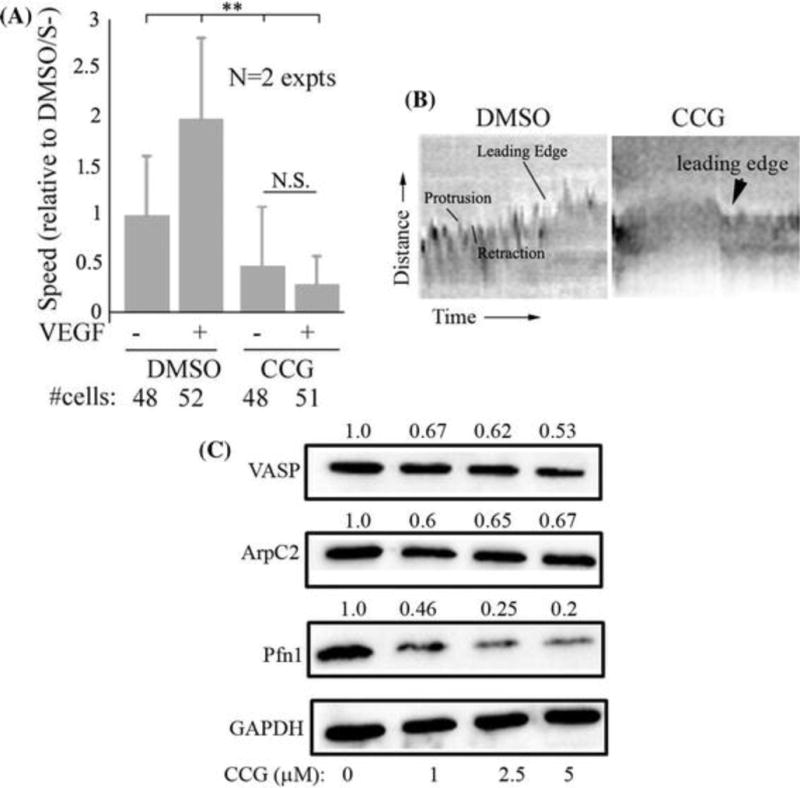
A) Quantitative analyses of the effect of 5 M CCG-1423 treatment on VEGF-induced motility of HmVEC (these data are based on time-lapse analyses of randomly migrating HmVEC cells for 2 hrs) (**: p<0.01; data summarized from 2 independent experiments; N.S: not significant; S-: serum-starved state). B) Representative images of kymograph traces of VEGF-stimulated cells under DMSO vs CCG-1423 (5 M) treatment. C) Representative immunoblots of HmVEC extracts for VASP, ArpC2, Pfn1, and GAPDH (loading control) at various concentrations of CCG-1423 treatment (the numbers indicate the expression level relative to DMSO control averaged from 2 independent experiments). HmVEC lysates were prepared at the same time-point as the end-point cord formation or cell motility assay.
