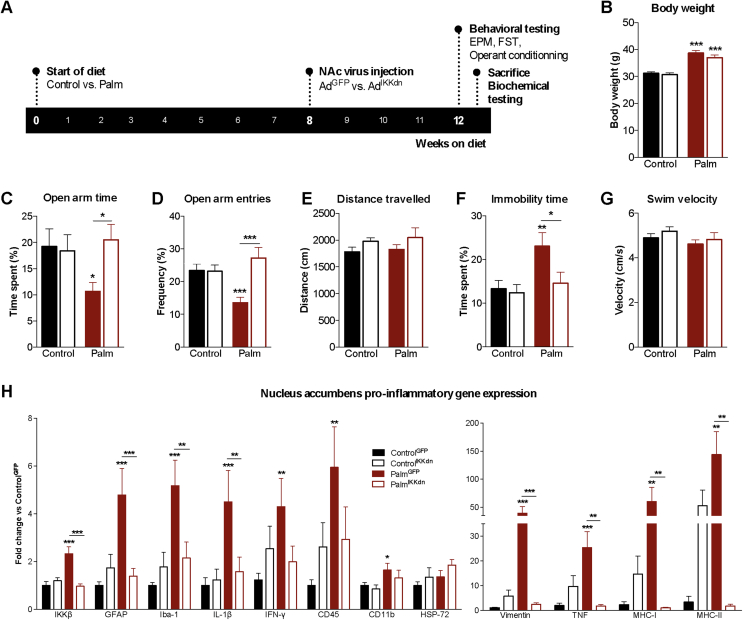
Figure 4.
Inhibition of IKKβ/NFkB in the nucleus accumbens prevents diet-induced anxiodepressive behavior and neuroinflammation. (A) Experimental layout depicting start of diets, viral injection and testing. (B) Final body weights after testing (n = 21–25/group). (C, D) Time spent and entries in open arms of the elevated-plus maze (n = 13–20/group). (E) Distance traveled in the elevated-plus maze. (F) Immobility time during the last 4 min of the forced swim test (n = 13–19/group). (G) Swimming velocity during the first 2 min of the forced swim test (n = 13–19/group). (H) Nucleus accumbens relative gene expression of inhibitor of kappa-B kinase-bêta (IKKβ), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule-1 (Iba-1), interleukin-1bêta (IL-1β), interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), CD45, CD11b, heat shock protein-72 (HSP-72) vimentin, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-1 and MHC-II (n = 7–9/group). Group mean ± SEM; two-way analysis of variance, Bonferroni post hoc; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005.