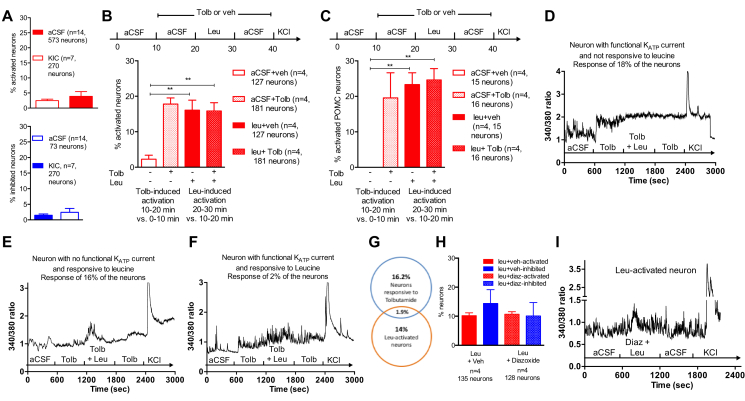
Figure 4.
Leucine-induced changes in [Ca2+]iare independent of leucine metabolism and KATPchannels. Effect of KIC exposure on neuronal activation and inhibition (A). Neuronal responses to tolbutamide and leucine exposures in neuronal mediobasal hypothalamic cultures (B) or arcuate POMC neurons (C). Changes in [Ca2+]i, as assessed by 340/380 nm fluorescence ratios in primary cultures of mediobasal hypothalamic neurons treated with leucine in the presence of Tolbutamide (D, E, F). Overlap between leucine-activated neurons and neurons sensitive to Tolbutamide (G). Effect of diazoxide (diaz) on leucine-induced neuronal activation and inhibition (H), and changes in [Ca2+]i, as assessed by 340/380 nm fluorescence ratios in primary cultures of mediobasal hypothalamic neurons treated with leucine in the presence of diazoxide (I). Data are means ± SEM. *: p < 0.05. **: p < 0.01.