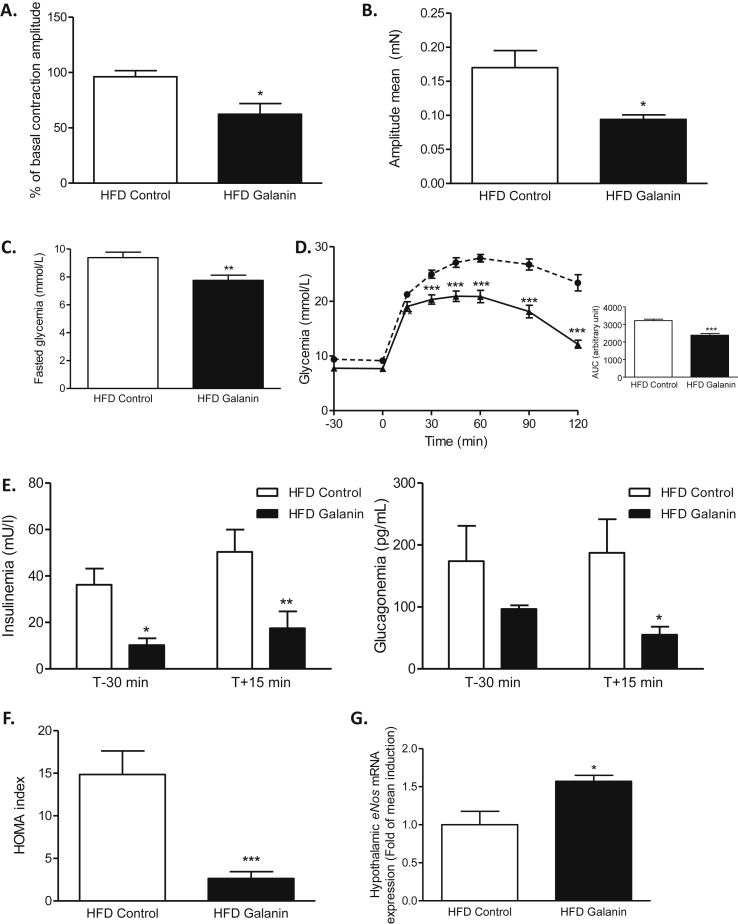
Figure 3.
Oral galanin treatment decreases the duodenal hyper-contractility of diabetic mice and improves diabetic state. (A)Ex vivo measurement of duodenal mechanical contraction amplitude in response to Krebs–Ringer (Control) or galanin 100 nM in high-fat diet (HFD) mice. n = 5 per group. *p < 0.05 vs HFD Control. (B)In vivo measurement of duodenal mechanical contraction amplitude in response to an oral administration of water (HFD Control) or galanin 100 nM during one week. n = 5–8 per group. *p < 0.05 vs HFD Control. (C) Effects of an oral administration of water (HFD Control) or galanin 100 nM during one week on fasted glycemia in HFD mice. n = 12–14 per group. **p < 0.01 vs HFD Control. (D) Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in 6 h fasted HFD mice, after an oral administration of water (HFD Control) or galanin 100 nM during one week. n = 12–14 per group. The adjacent graph represents the average area under the curve (AUC) ***p < 0.001 vs HFD Control. (E) OGTT-associated plasma insulin and glucagon 30 min before and 15 min after oral load of glucose after an oral administration of water (HFD Control) or galanin 100 nM during one week. n = 5 per group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs HFD Control. (F) OGTT-associated insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) in 6 h fasted HFD mice after an oral administration of water (HFD Control) or galanin 100 nM during one week. n = 5 per group. ***p < 0.001 vs HFD Control. (G) Relative expression of endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) mRNA in hypothalamus of HFD mice after an oral administration of water (HFD Control) or galanin 100 nM during one week. n = 4–5 per group.