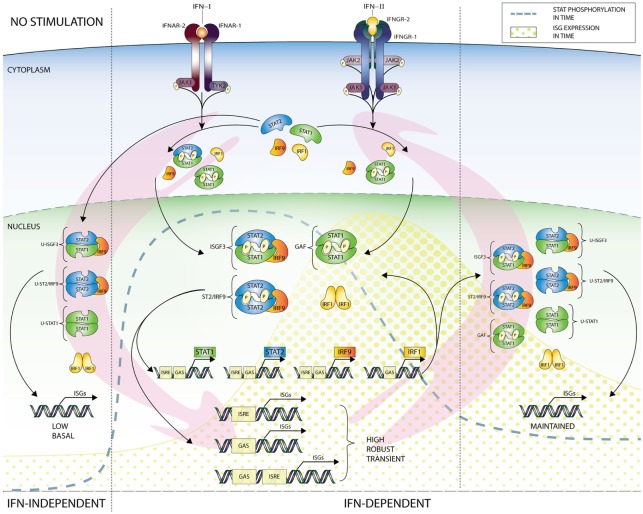
Figure 5.
Cooperation of unphosphorylated and phosphorylated ISGF3 and GAF components and IRF1 in the regulation of basal and IFN-induced transcription. In unstimulated cells, most of the known ISGs are expressed at low but detectable levels. Among these genes, there are examples of components (STATs and IRFs) of transcription factors, which in the absence of stimulation can combine in unphosphorylated complexes (U-ISGF3, U-STAT1, U-STAT2/IRF9, and IRF1) and drive the constitutive expression of ISGs. After cell stimulation with IFN type I or II, receptors dimerize and enable receptor-bound kinases (JAK1 and TYK2 for IFN-I or JAK1 and JAK2 for IFN-II) transphosphorylation and STAT protein recruitment. Next step is phosphorylation of STATs, which can now dimerize and with or without a partner (IRF9) create complexes—ISGF3, ST2/IRF9, and GAF, then translocate to the nucleus and start a high and robust but transient expression (yellow dotted graph) of GAS and/or ISRE-containing ISGs. This leads to, inter alia, rapid accumulation of newly synthesized STAT1, STAT2, IRF9, and IRF1 proteins in the cytoplasm, which can create new transcription factors in unphosphorylated form (U-ISGF3, U-STAT1, and U-STAT2/IRF9), and while level of phospho-proteins is dropping (dotted line) support or take over the role of phosphorylated complexes in sustaining the expression of ISGs. Important role in the circuit plays IRF1, which can occupy ISRE-containing genes and co-binds with other factors to modulate IFN-induced response, as well as basal ISG expression. As shown in the graph, responses to both types of IFN rely on common elements and events of the JAK–STAT signaling pathway and result in partially shared outcome. Thus, IFN-I and IFN-II induce a common as well as a unique set of genes. These facts clearly point to functional and biological overlap between IFN-I and IFN-II action and additionally to existence of mechanisms allowing cells to manage and adjust both responses. Abbreviations: IFN, interferon; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; JAK, Janus kinase; TYK, tyrosine kinase; ISGF3, interferon-stimulated gene factor 3; GAF, γ-activated factor; ISRE, interferon-stimulated response element; GAS, γ-activated sequence; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene; P, phosphate; U, unphosphorylated form.