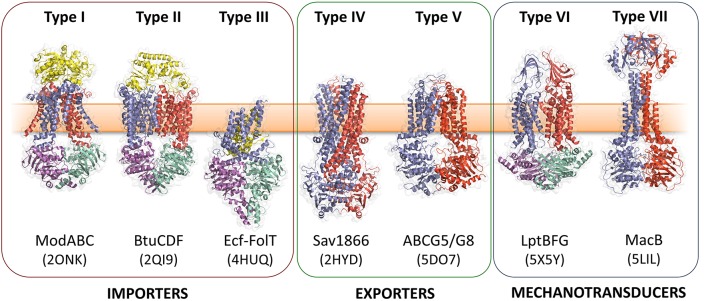
Figure 1.
Seven ABC transporter superfamilies. A single representative from each superfamily is shown colored by protein chain. PDB identifiers are given in parentheses. The seven ABC folds are here further divided into three “classes” based on function. Families I-III are importers, Type IV and V are exporters and Types VI and VII are mechanotransducers. Note that the two ABC exporter families here termed Type IV and Type V are also sometimes referred to as type I and II ABC exporters. From left to right: the molybdate transporter (Hollenstein et al., 2007) (ModABC), vitamin B12 transporter (Korkhov et al., 2012) (BtuCDF), folate importer (Xu et al., 2013) (Ecf-FolT), multidrug exporter (Dawson and Locher, 2006) (Sav1866), the sterol transporter (Lee et al., 2016) (ABCG5/G8), the lipopolysaccharide extractor (Luo et al., 2017) (LptBFG) and the enterotoxin and macrolide transporter (Crow et al., 2017) (MacB). Folds are named by extension of a previously established convention (ter Beek et al., 2014). Adapted from Crow et al. (2017).