Figure 4.
The rs7163757 Risk Allele (C) Exhibits 2-fold Higher Enhancer Activity Than the Non-risk Allele (T)
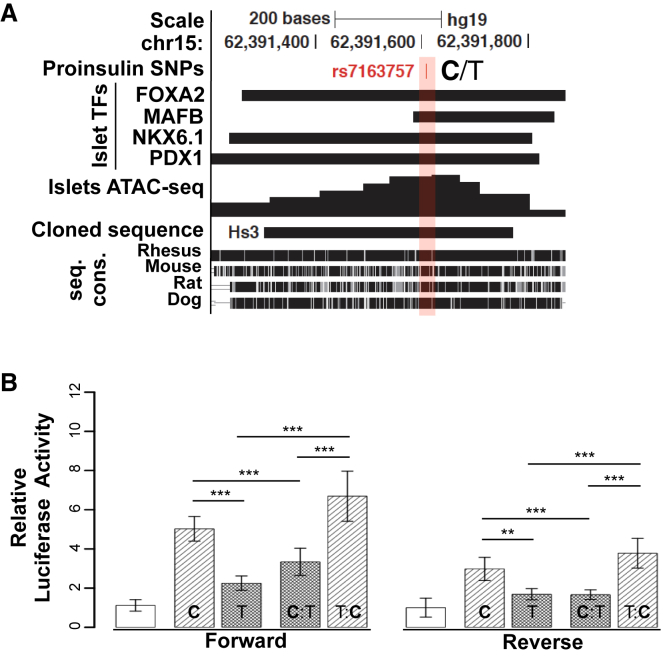
(A) UCSC Genome Browser view of islet SE constituent HS3. Islet TF ChIP-seq,18 ATAC-seq pileup, and cross-species sequence conservation (seq. cons.) are indicated. Proinsulin- and T2D-associated rs7163757 (C/T) is indicated by red shading and font. The DNA sequence cloned and tested for enhancer activity is indicated. UCSC Genome Browser coordinates correspond to hg19.
(B) Luciferase reporter assay of the HS3 sequences (cloned in forward and reverse orientations) containing the rs7163757 risk allele (C) or non-risk allele (T) (haplotype 1 or 2, respectively), the C allele mutated to the T allele (C:T), and vice versa (T:C). All luciferase activity was normalized to that of the empty vector. HS3 enhancer activity was compared with the normalized activity of the pGL4.23 vector containing Gateway sequence in the forward and reverse orientations. All cloned HS3 enhancer sequences were significantly more active than the control vectors (p values not indicated). p values are indicated for the HS3 C allele versus T allele, the T allele versus T:C, the C allele versus C:T, and T:C versus C:T in the forward and reverse orientations. There was no significant difference between mutated alleles T:C and C and between C:T and versus T (p values not indicated). Each construct was measured in triplicate; a total of 16 biological replicates were measured per haplotype over seven independent experiments. Data represent the mean ± SEM; ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (two-sided unpaired t test).