Figure 5.
Islet C2CD4B and C2CD4A Expression Is Increased by the rs7163757 T2D Risk Allele (C) and Induced by Diabetogenic Inflammatory Cytokines
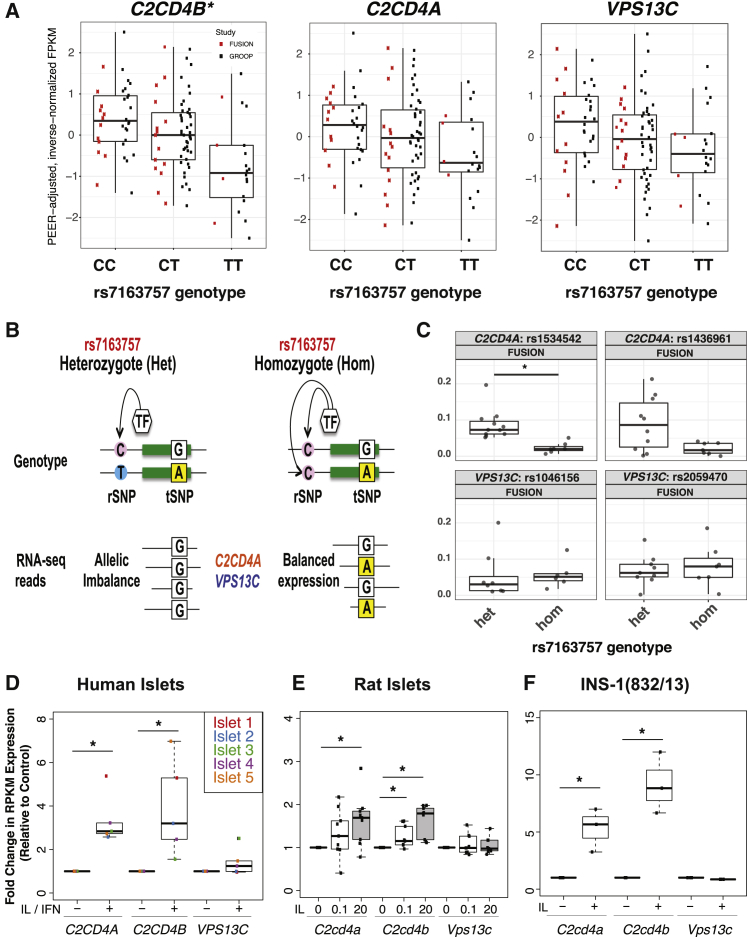
(A) Boxplots of C2CD4B, C2CD4A, and VPS13C expression (PEER-adjusted, inverse-normalized FPKM) in 112 human islets grouped by rs7163757 genotype. Red and black dots indicate FPKM values from FUSION and Groop islet cohorts, respectively; the asterisk indicates a genome-wide significant association (see also Table S10).
(B) Schematic depicting the principles of AEI. The heterozygous rSNP genotype leads to an expression imbalance of the tSNP in RNA-seq data for genes regulated by the rSNP (left). The homozygous rSNP genotype manifests as equivalent transcription of both tSNP alleles.
(C) AEI between rSNP rs7163757 and tSNPs in C2CD4A and VPS13C in FUSION human pancreatic islet RNA-seq data. Dots indicate the value of each islet sample, which have been grouped into heterozygous (Het) and homozygous (Hom) rs7163757 genotypes on the x axis. The absolute value of allelic imbalance for each tSNP is indicated on the y axis; ∗q < 0.05 (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test adjusted for multiple testing) (see Material and Methods and Table S11). C2CD4A, not VPS13C, exhibits a rs7163757 genotype-dependent allelic imbalance, as depicted schematically in (B).
(D–F) C2CD4A, C2CD4B, and VPS13C expression in (D) human islets before and after IL-1β (IL) and IFN-γ (IFN) exposure,48 (E) rat islets exposed to 0, 0.1, or 20 ng/mL IL-1β,49 or (F) INS-1(832/13) cells exposed to 2 U/mL IL-1β for 2 hr. Boxplots represent fold changes in expression (RPKM) in relation to that of untreated controls; ∗p < 0.05 (Wilcoxon rank-sum test).