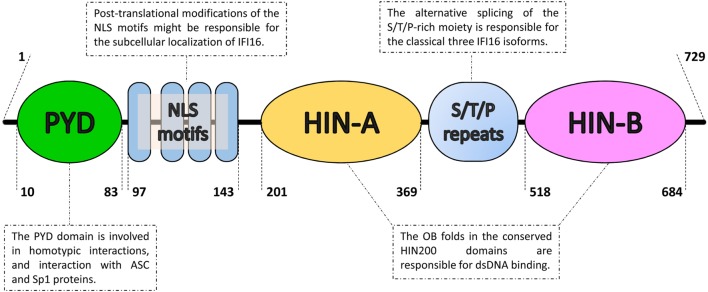
Figure 1.
Domain organization of the IFN-inducible protein 16 (IFI16). From the N- to the C-terminal (left to right), IFI16 comprises a pyrin domain (PYD) involved in protein–protein interactions, a linker region containing four nuclear localization signal motifs (NLS) and two hematopoietic interferon-inducible nuclear protein with 200-amino-acid repeats (HIN200) domains, which is an hallmark of the absent in melanoma 2-like receptors/PYHIN proteins. The HIN200 domains include two tandem b-barrels, known as oligonucleotide–oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which allow DNA docking in a non-sequence-specific manner. They are separated by serine/threonine/proline-rich (S/T/P) repeats, which are regulated by alternative mRNA splicing. The numbers represent the amino acid positions based on NCBI Reference Sequence NP_005522.2.