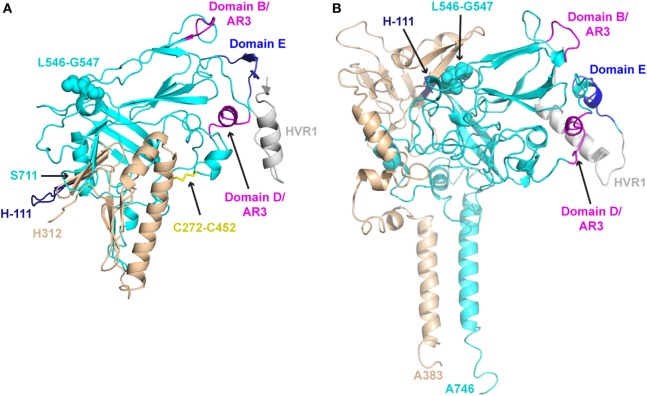
Figure 2.
Structural models of E1E2 heterodimeric assembly. (A) E1E2 model from Castelli et al. (E1E2-C) (64) in comparison with (B) E1E2 model from Freedman et al. (E1E2-F) (65), oriented in the same frame of reference based on E2 core regions. E1 and E2 glycoproteins are shown as tan and cyan cartoons, respectively, while key epitopes are colored and labeled, as in Figure 1: H-111 epitope at N-terminus of E1 (“H-111,” aa 192–202, dark blue), E2 hypervariable region 1 (HVR1, aa 384–410, gray), Domain E (aa 412–423, blue), Domain D/AR3 (aa 434–446, magenta), Domain B/AR3 (aa 529–535, magenta). Additionally, selected features of modeled E1E2 are highlighted: the predicted E1–E2 disulfide bond of E1E2-C (C272–C452), shown as yellow sticks, and E2 residues L546–G547, predicted to interact with E1 in E1E2-F model, are shown in spacefill on both models. C-terminal residues of E1 and E2 are also labeled for both models (H312, S711 for E1E2-C, A383, A746 for E1E2-F).