Figure 3.
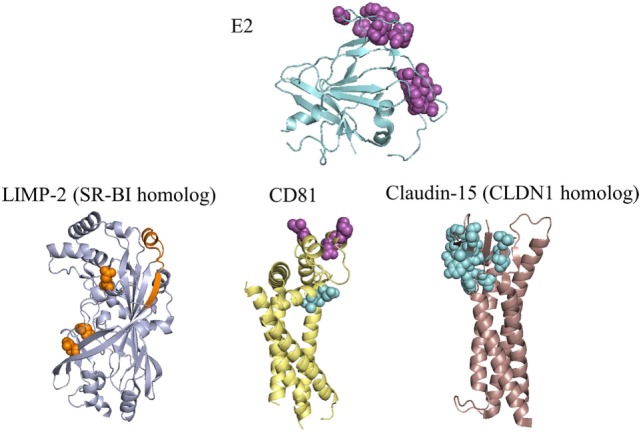
Residues of E2 and coreceptors that influence hepatitis C virus (HCV) entry and infection. E2 and three receptors are depicted with the most complete crystal structure available, or with a crystal structure of a homologous receptor. Purple spacefill residues on E2 showed <20% binding to CD81 when substituted to alanine (81, 105); residues with the same color and representation on CD81 showed reduced or eliminated binding to soluble E2 during random mutagenesis (100). Orange spacefill residues on LIMP-2 showed reduced binding to soluble E2 when mutated to a non-synonymous coding variant or the corresponding residue for mouse SR-BI (106, 107). Binding determinants of E2 to SR-BI are present in HVR1 (108), and are not present on the E2 crystal structure. Cyan spacefill residues on CD81 showed reduced association with CLDN1 when mutated to alanine (67), while cyan spacefill residues on CLDN1 showed either reduced binding to CD81 or decreased entry of HCVpp in alanine substitutions (67, 97, 109). PDB codes used are: 4MWF (E2), 5TCX (CD81), 4F7B (LIMP-2, representing SR-BI), and 4P79 (mouse claudin-15, representing claudin-1). SR-BI and CLDN1 have only moderate sequence identities to their structurally characterized homologs (LIMP-2 has 34% identity with SR-BI, mouse claudin-15 has 35% identity with human CLDN1), thus structures of these receptors may differ from the homologs shown.
