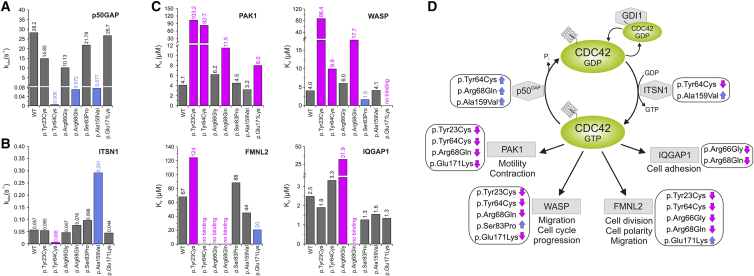
Figure 2.
Assessment of the GTPase Activity, Nucleotide Exchange, and Binding to Effectors of Disease-Causing CDC42 Mutants
(A) Mean rate constants (kobs values) of p50GAP-stimulated GTP hydrolysis. Grey bars indicate non-significant differences compared to wild-type CDC42; blue bars indicate abolished/impaired GTP hydrolysis, which in turn results in an increased amount of active, GTP-bound CDC42 and thus enhanced signal flow. Data were obtained from >4 independent experiments.
(B) Mean rate constants (kobs values) of the GEF-catalyzed release of labeled GDP (mantGDP). Grey bars indicate non-significant differences compared to wild-type CDC42; blue and magenta bars indicate increased or abolished nucleotide exchange, respectively. The former is predicted to promote enhanced signaling, while the latter blocks CDC42 in its inactive state. Data were obtained from >4 independent experiments.
(C) CDC42 mutants variably affect binding to effectors. Dissociation constants (Kd) obtained for the interaction of CDC42 proteins with PAK1, WASP, IQGAP1, and FMNL2 determined by fluorescence polarization. Data were collected from titration of increasing concentrations of the respective effectors. They were obtained from >4 independent experiments and are illustrated as bar charts. Grey bars indicate non-significant differences compared to wild-type CDC42; blue and magenta bars indicate increased or decreased binding affinity, respectively.
(D) Scheme summarizing the functional dysregulation of disease-causing mutants on downstream signaling pathways and cellular processes. ITSN1 is a specific GEF for CDC42 promoting the active state of the GTPase by catalyzing GDP release. p50GAP negatively controls CDC42 function by stimulating the GTP hydrolysis reaction. CDC42 interaction with PAK1, WASP, FMNL2, and IQGAP1 activates signaling pathways controlling different cellular processes. For each specific function, the blue and magenta arrows indicate the hyperactive or defective behavior, respectively.