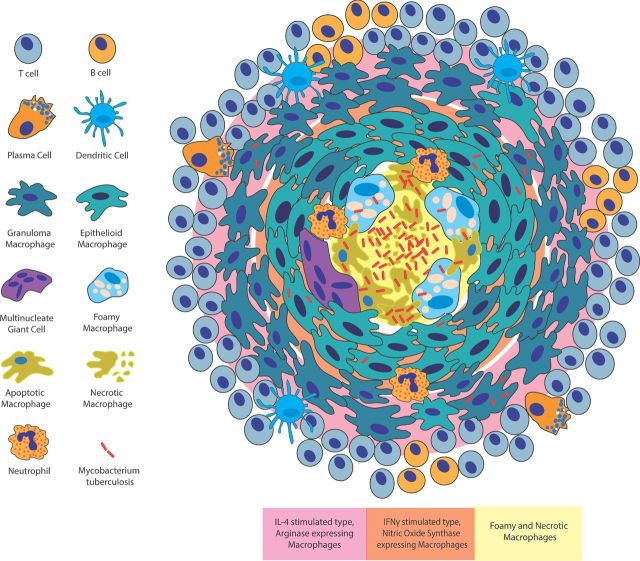
Figure 2.
Structure and inflammatory arrangement of the tuberculosis granuloma. The granuloma is an organized aggregate of macrophages surrounded by a cuff of B and T lymphocytes. Plasma cells and dendritic cells are also granuloma associated. Within the granuloma, macrophages differentiate into additional cell types including epithelioid macrophages, MGCs and foamy macrophages. Different cell types are spatially organized within the granuloma with foamy macrophages found surrounding the necrotic lipid-rich core, epithelioid macrophages forming tight junctions around the central core and additional macrophages aggregating at the outer edge of the structure. The activation state of macrophages as well as the presence of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers is also spatially arranged with more anti-inflammatory phenotypes at the periphery of the granuloma structure (pink) and more pro-inflammatory phenotypes in central regions (orange).