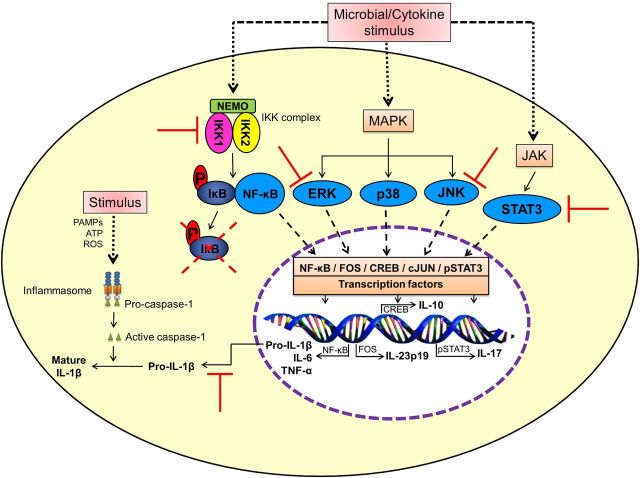
Figure 2.
Celastrol inhibits NF-κB and other cell signaling pathways associated with inflammation. Celastrol inhibits NF-κB activation via inhibition of IKK activity as well as degradation and phosphorylation of IκBα; inhibits the phosphorylation of ERK, JNK and STAT3, which regulate other nuclear transcription factors; and inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17). The effect of celastrol on mature IL-1β production is primarily owing to reduction of pro-IL-1β production via inhibition of NF-κB. (CREB—cAMP response element-binding protein; ERK—extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IKK—IκB kinase; JNK—c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK—mitogen-activated protein kinase; NEMO—NF-κB essential modulator; NF-κB—nuclear factor-kappa B; P—phosphorylated; PAMPs—pathogen-associated molecular patterns; STAT3—signal transducer and activator of transcription 3).