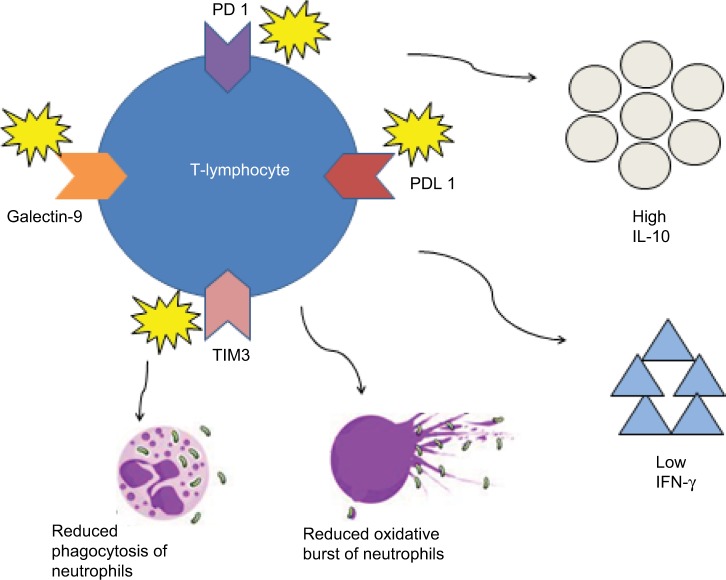
Figure 1.
Pathophysiology for immunosuppression in severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Notes: Higher chronic lipopolysaccharide exposure leads to overexpression of inhibitory receptors (PD 1, PDL 1, TIM3 and galectin-9) on T lymphocytes resulting in higher IL-10 and lower IFN-γ production as well as reduced neutrophil antimicrobial activities (e.g., phagocytosis and oxidative burst).
Abbreviations: IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL-10, interleukin-10; PD 1, programmed cell death protein 1; PDL 1, programmed death ligand 1; TIM3, T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3.