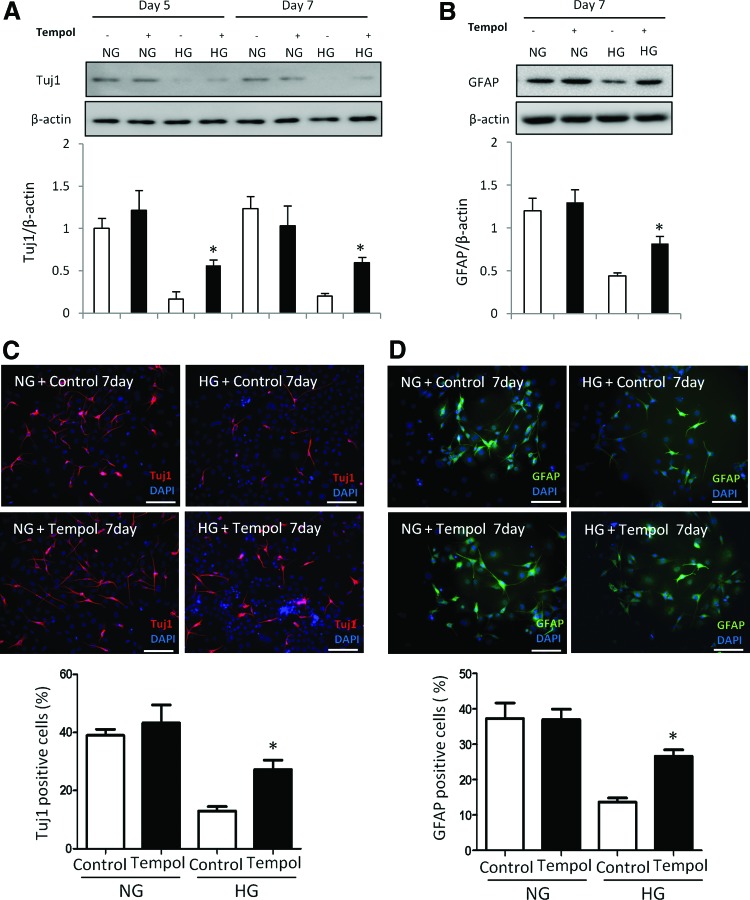
FIG. 2.
Oxidative stress mediates the inhibitory effect of high glucose on neural differentiation. An antioxidant reverses high glucose-inhibited neural differentiation. C17.2 cells were differentiated at NG (5 mM) or HG (25 mM), with or without Tempol (100 μM) for 5 and 7 days. Tempol stock solution (100 mM) was prepared by dissolving in water. During cell differentiation, Tempol was added to the differentiating C17.2 cells at a final concentration of 100 μM. Same volume of vehicle was added into the controls. Protein levels of Tuj1 (A) and GFAP (B) determined by immunoblotting. The quantification of the data was shown in the bar graph. Immunostaining of Tuj1 (C) or GFAP (D) in the NG, NG plus Tempol, HG, HG plus Tempol groups and quantification for numbers of Tuj1 or GFAP positive cells. Bars = 100 μm. All experiments were repeated three times (n = 3). Values are the mean ± SE from three separate experiments. *Indicates significant differences (P < 0.05) compared to the normal glucose (5 mM) group. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd