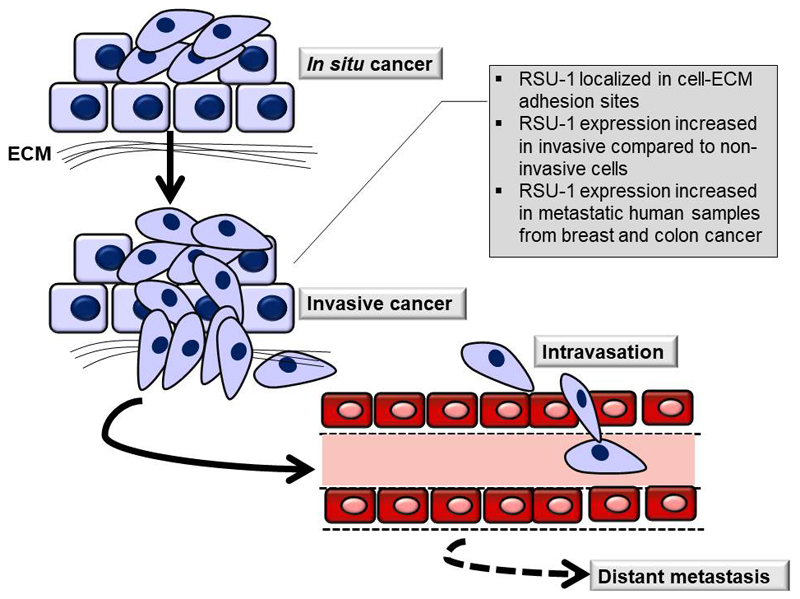
Figure 1. Schematic showing the initial stages of metastasis where RSU-1 is involved.
Cancer cells in in situ cancer proliferate within the tumor while in invasive cancer cell adhesion is disrupted and cells dissociate from the original tumor to migrate and invade through surrounding tissues until they reach the circulation. Once in circulation, cells are transferred to distant sites of the body where they colonize the sites and form metastasis. RSU-1 localizes to cell-ECM adhesions and its expression is increased in invasive compared to non-invasive cells.