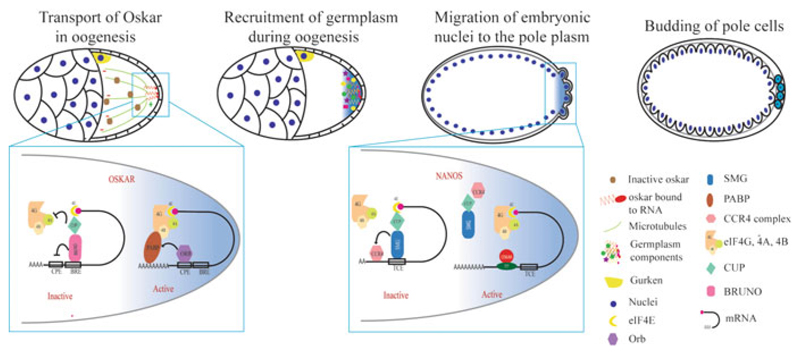
Fig. 6.1.
Translational control during germ cell specification in Drosophila. Germplasm is assembled during oogenesis by Oskar. oskar mRNA is transported in an inactive form and deposited at the posterior pole where its translation is activated. oskar translation is suppressed by Bruno with the help of Cup. At the posterior, oskar translation is activated by ORB; ORB recruits PABP and facilitates translational activation. Oskar further recruits other germplasm components during late stages of oogenesis. The early Drosophila embryo is a syncytium; at the start of cellularization, some of the posterior nuclei and the surrounding germplasm form the pole cells (PGCs) by budding. nanos mRNA is translationally suppressed in the anterior region by Smaug (Smg) which recruits Cup and prevents translation initiation. At the posterior end, nos mRNA is bound by Oskar, which prevents Smg from binding to nos-2 3′ UTR, which derepresses nos mRNA. Smaller cells diagrammed in the top left two cartoons represent the nurse cells