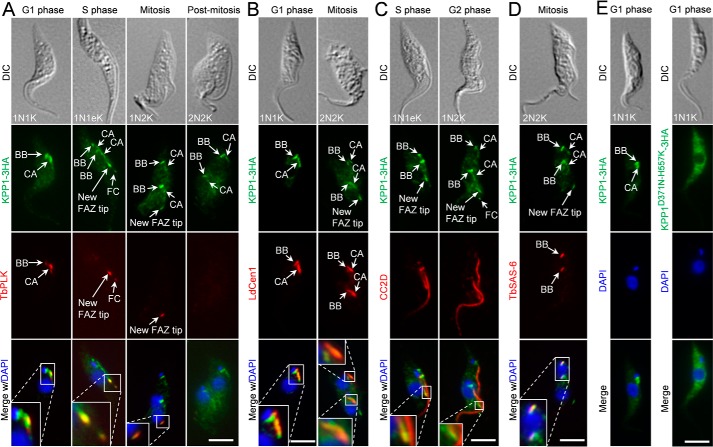
Figure 2.
KPP1 localizes to multiple flagellum-associated structures and co-localizes with TbPLK at the basal body, the centrin arm, and the new FAZ tip. A, subcellular localization of KPP1 during the cell cycle and co-localization of KPP1 with TbPLK. KPP1 was endogenously tagged with a triple HA epitope and detected by FITC-conjugated anti-HA mAb, whereas TbPLK was detected by anti-TbPLK pAb. Cells were counterstained by DAPI for nuclear and kinetoplast DNA. BB, basal body; CA, centrin arm; FC, flagella connector. Scale bar, 5 μm. B, KPP1 localizes to the basal body and the centrin arm. Shown are the co-immunostaining of cells with FITC-conjugated anti-HA mAb to detect KPP1–3HA and anti-LdCen1 pAb to label the basal body and the centrin arm. Scale bar, 5 μm. C and D, KPP1 localizes to the new FAZ tip and the basal body. Shown in C are an S-phase cell and a G2 cell co-immunostained with FITC-conjugated anti-HA mAb to detect KPP1–3HA and anti-CC2D pAb to label the FAZ, and shown in D is a mitotic cell co-immunostained with FITC-conjugated anti-HA mAb to detect KPP1–3HA and anti-TbSAS6 pAb to label the basal body. E, localization of triple HA-tagged wild-type KPP1 and a mutant KPP1 bearing two point mutations in the active sites. Cells were immunostained with FITC-conjugated anti-HA mAb and counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars, 5 μm.