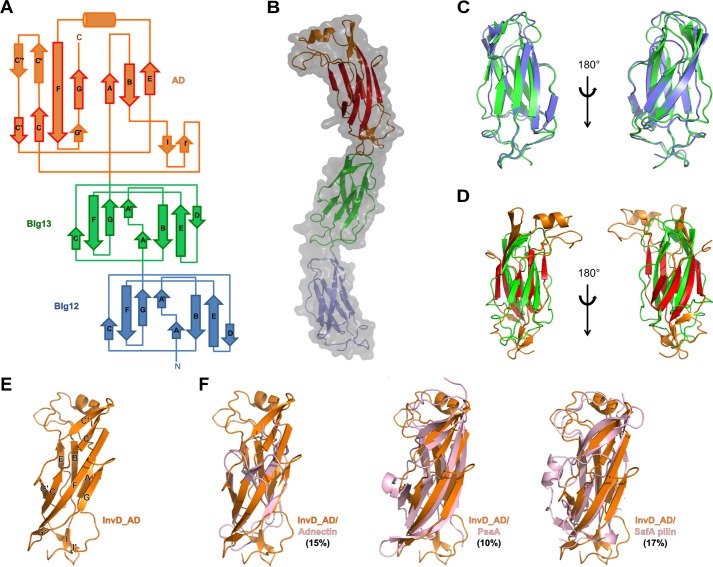
Figure 2.
Architecture of InvD1640 domains. A, topology diagram of BIg12/13 and AD of InvD1640 with the β-strand nomenclature according to the immunoglobulin superfamily fold. β-Strands in BIg12/13 as well as β-strands shown with a red border in the AD correspond to the canonical β-strands in the immunoglobulin superfamily. Noncanonical modifications and insertions of secondary structure elements into the immunoglobulin superfamily core structure of the AD are shown with an orange border. B, overlay of surface and cartoon representation of the X-ray crystal structure of InvD1640. In the AD, β-strands representing the canonical immunoglobulin superfamily fold are shown in red, whereas noncanonical modifications/insertions are shown in orange. C, superposition of BIg12 and BIg13 shown in two orientations. D, superposition of BIg13 and the AD shown in two orientations. E, cartoon representation of InvD–AD with β-strands labeled as shown in A. F, structural comparison of InvD–AD with other structurally similar proteins. Superposition of InvD–AD (orange) was with following proteins (in pink): adnectin (PDB code 4OV6:G) (r.m.s.d. 4.3 Å); PsaA (PDB code 4F8O:A) (r.m.s.d. 3.7 Å); and SafA pilin (PDB code-2CNY:A) (r.m.s.d. 3.7 Å). Structural comparison was done by using the PDBeFold program (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd-srv/ssm; please note that the JBC is not responsible for the long-term archiving and maintenance of this site or any other third party hosted site.). Numbers in parentheses correspond to the percentage of sequence identity between the two superposed proteins.