Figure 8.
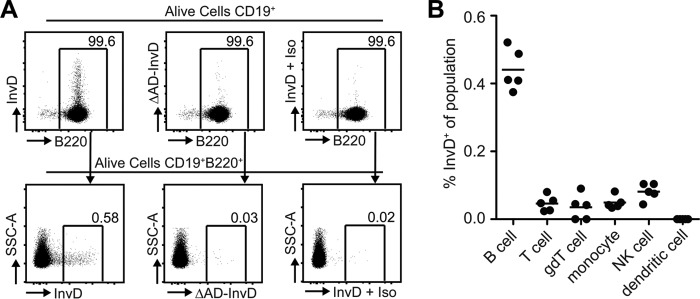
InvD binds predominantly to B cells. A, InvD1640 binds to 0.58% of the B cell population, whereas ΔAD-InvD or the isotype control show a strongly reduced binding to 0.03 and 0.02% of the B cell population, respectively. Single cell suspensions from spleens were analyzed using flow cytometry. Previous to B220+ gating, B cells were gated as alive cells, excluded for duplets, and gated on CD19+ cells. Numbers indicate frequency of parental population. Anti-FLAG allophycocyanin antibody was used to detect the 3×FLAG-tagged InvD1640. Exemplary dot plots depict frequencies and fluorescence intensity of 3×FLAG-tagged InvD1640 or 3×FLAG-tagged ΔAD-InvD on living B cells using anti-FLAG-antibody conjugated to allophycocyanin. Isotype controls were performed using 3×FLAG-tagged InvD1640 and subsequently subjecting the cells to allophycocyanin-conjugated anti-FLAG-antibody isotype control antibody (InvD + Iso). Exemplary data of five independent experiments. B, scatterplot summarizes frequencies of InvD+ cells of the respective cell population. Pooled data of two independent experiments (n = 2–3 mice per experiment) are shown. B cells, CD19+; T cells, CD3+; γδT cells, CD19−γδTCR+; NK cells, CD49b+; monocytes, CD19−γδTCR−CD11b+CD11c−; dendritic cells, CD19−γδTCR−CD11bmedCD11c+.