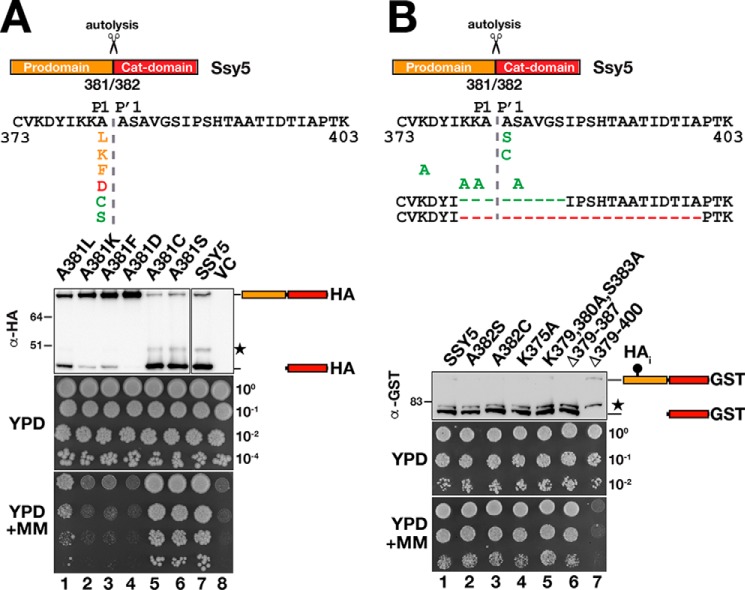
Figure 7.
Ssy5 autolysis exhibits a less strict sequence requirement. Mutational analysis of the Ssy5 autoprocessing site was performed. Shown is a schematic presentation of Ssy5 expanding the sequence between amino acids 373 and 403 and including single amino acid substitutions at the P1 and P′1 positions, at other positions and deletions, as indicated. Mutations that block (red), impair (orange), or do not affect autolysis (green) are indicated. A, immunoblot analysis of extracts and growth of HKY77 (ssy5Δ) carrying plasmids pAM105 (A381L), pAM106 (A381K), pAM107 (A381F), pAM108 (A381D), pAM109 (A381C), pAM110 (A381S), pCA177 (SSY5), or pRS316 (VC). Immunoreactive forms of HA-tagged Ssy5 are indicated at their corresponding position of migration. The position of an unrelated cross-reacting protein is marked with a star. Ssy5 function was assessed by a growth-based assay, and 10-fold dilutions of cultures grown in SD were spotted onto YPD and YPD+MM. B, immunoblot analysis of extracts and growth of the CAY265 (ssy5Δ) carrying plasmids pSH120 (SSY5), pSH091 (A382S), pSH093 (A382C), pSH127 (K375A), pSH117 (K379A, K380A, and S383A), pSH128 (Δ379–387), or pSH129 (Δ379–400). Immunoreactive forms of Ssy5-GST are indicated at their corresponding position of migration. The position of an unrelated cross-reacting protein is marked with a star. Ssy5 function was assessed by growth on YPD and YPD+MM as in A. Molecular markers (kDa) are indicated at the position of migration (left of immunoblots).