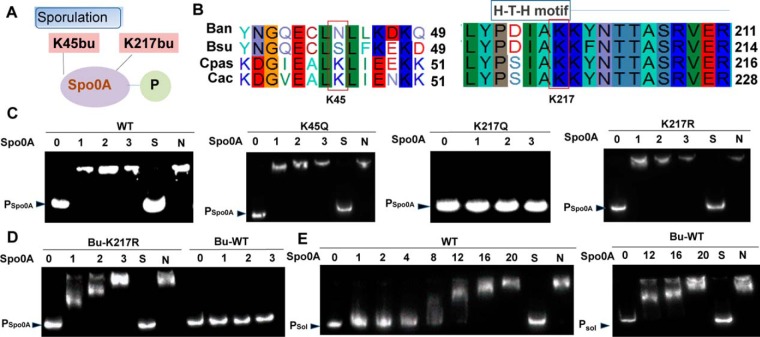
Fig. 7.
Regulation of Spo0A by lysine butyrylation. A, The two butyrylation sites identified in the transcription factor Spo0A of C. acetobutylicum strain. B, Sequence alignment of Spo0A, from Bacillus anthracis (Ban), Bacillus subtilis (Bsu), Clostridium pasteurianum (Cpas) and Clostridium acetobutylicum (Cac). C, DNA-binding abilities of Spo0A and derivatives by EMSA. The amount of His-Spo0A used (10−7 × g) is shown at the top of each lane. From left to right panel: wild type Spo0A, Spo0A K45Q, Spo0A K217Q and Spo0A K217R. D, DNA-binding abilities of Bu-Spo0A and Bu-Spo0A K217R. The amount of His-Spo0A used (10−7 × g) is shown at the top of each lane. Left panel: The Bu-Spo0A K217R was incubated with probes. Right panel: Bu-Spo0A was incubated with probes. E, DNA-binding abilities of wt and Bu-wt. The amount of His-Spo0A used (10−7 × g) is shown at the top of each lane. Left panel: The wt was incubated with probes. Right panel: Bu-wt was incubated with probes.