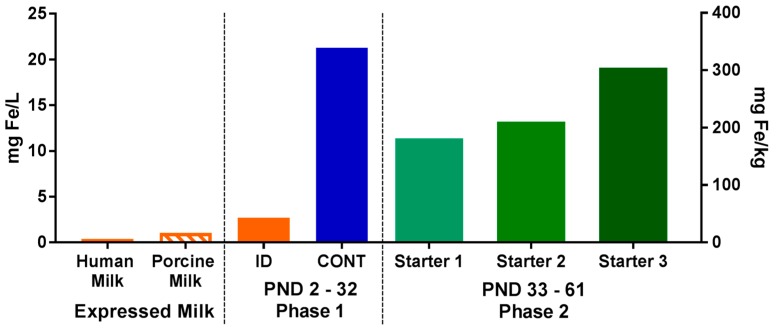
Figure 1.
Analyzed concentrations of iron in porcine and human milks, as well as in dietary treatments during both phases of the pig study. During phase 1, pigs were fed either a control (CONT) or iron-deficient (ID) milk replacer. The CONT treatment contained 21.3 mg/L (106.3 mg/kg), and the ID treatment contained 2.72 mg/L (13.6 mg/kg). The ID treatment closely resembled the average iron content of porcine milk (n = 7; 1.06 mg/L) collected during a prior study [18], and is comparable to the iron concentration of human milk [7,19]. During phase 2, all pigs were fed a series of standard commercial starter diets (180–300 mg/kg). Abbreviations: CONT, control; ID, iron deficient; PND, postnatal day.