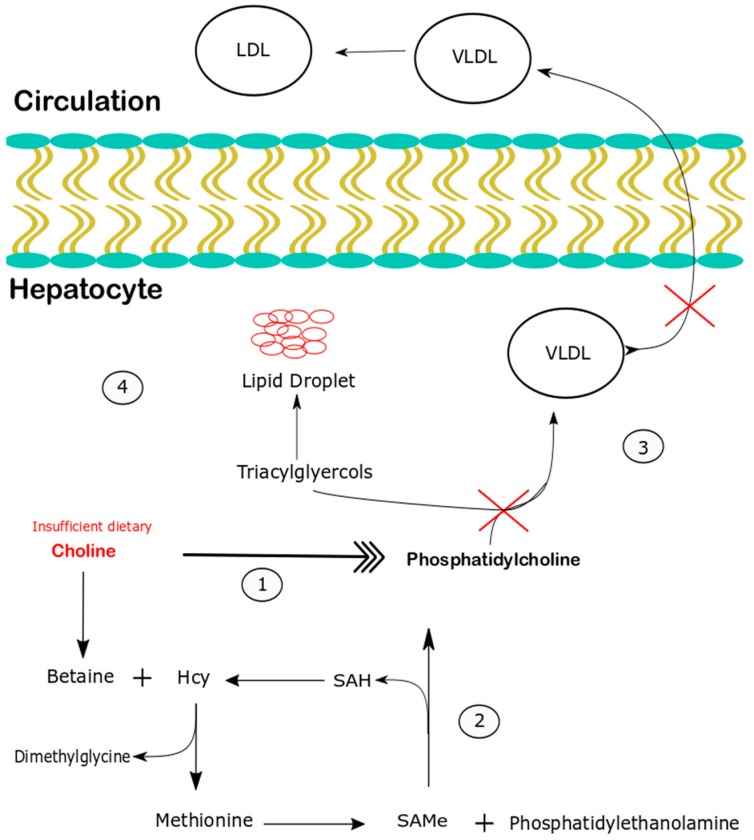
Figure 5.
Dietary choline supports the production of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and VLDL export from hepatocytes through two pathways; (1) Choline provides direct support for the CDP-choline pathway, in which choline is incorporated into the choline headgroup of PC, and (2) Choline indirectly supports PC synthesis by the phosphatidylethanolamine N-transferase pathway, in which choline is oxidized to betaine, a methyl donor that increases the availability of labile methyl groups for the trimethylation of phosphatidylethanolamine to PC. (3) PC produced through the PEMT and CDP-choline pathways supports the formation and secretion of VLDL. (4) When choline intake is insufficient to maintain PC synthesis, VLDL synthesis and export are impaired (indicated by red hash marks), resulting in triacylglycerol accumulations in the form of lipid droplets.