Figure 2.
PACS2 Variant Location
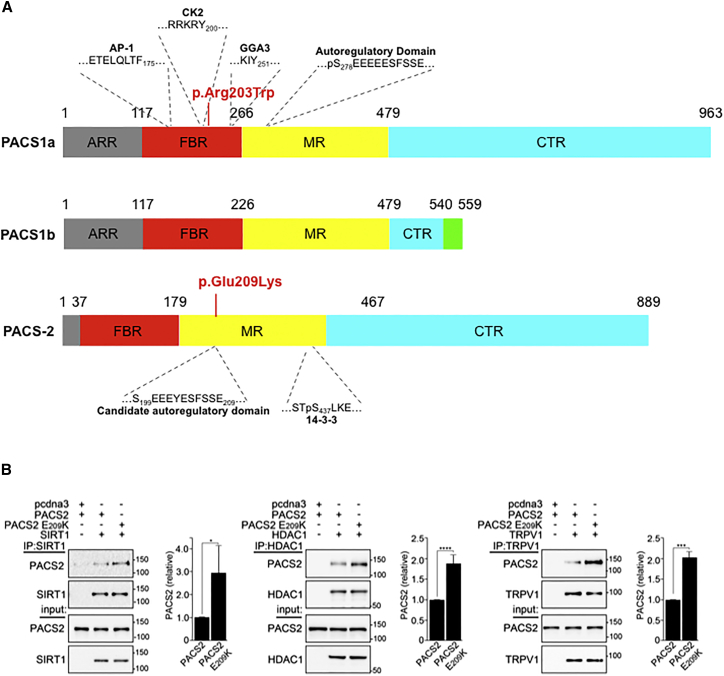
(A) Schematic of PACS1 and PACS2 illustrating the proposed domains (ARR, atrophin-1-related region; FBR, furin (cargo)-binding region; MR, middle region; CTR, C-terminal region) and residues important for partner protein binding (AP-1, adaptor protein complex 1; CK2, protein kinase CK2; GGA, Golgi-associated γ-adaptin ear homology domain ARF-interacting protein), with location of PACS1 and PACS2 missense variants responsible for intellectual disability.
(B) HCT116 cells, which can be efficiently transfected with plasmids, expressing the indicated proteins were harvested in mRIPA (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.0] plus 1% NP-40, 1% deoxycholate, and 150 mM NaCl) containing proteinase inhibitors (0.5 mM PMSF, 0.1 μM each of aprotinin, E-64, and leupeptin) and phosphatase inhibitors (1 mM Na3VO4 and 20 mM NaF). The FLAG-tagged cargo proteins SIRT1, HDAC1, or TRPV1 were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody (Sigma #F7425) and co-precipitating HA-tagged PACS2 or PACS2 p.Glu209Lys was detected by western blot using anti-HA antibody (Cell Signaling Technology #3724S) and developed with the Pierce ECL Western Blotting Substrate (ThermoFisher) using a FluorChem E image acquisition system (ProteinSimple). Signals were quantified using the AlphaView image analysis software package (ProteinSimple) and normalized to wild-type PACS2. Data are mean ± standard deviation, n = 4.