Figure 1.
A Framework for Massively Parallel Functional Testing of PTEN Mutations
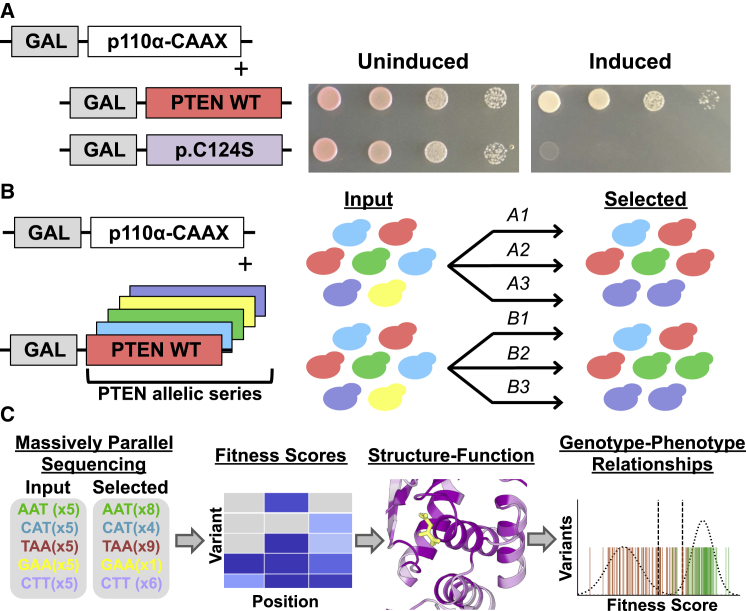
(A) Humanized yeast model for evaluating the effect of PTEN mutations on lipid phosphatase activity. Exogenous expression of the catalytic subunit of human PI3K with a membrane-targeting prenylation box motif (p110α-CAAX) in yeast is toxic. However, co-expression of human PTEN wild-type, but not catalytically dead PTEN p.Cys124Ser, can rescue growth. Both genes are under the control of a galactose inducible promoter (GAL).
(B and C) Modifications to allow massively parallel variant assessment.
(B) We generated a comprehensive PTEN allelic series, introduced these variants into yeast en masse, and subjected them to p110α-CAAX-mediated selection in liquid culture. We performed two biological replicates, each consisting of three technical replicates.
(C) We collected input and selected time points and subjected these to deep sequencing. We used read counts to calculate fitness scores and used these scores to highlight structure-function insights as well as genotype-phenotype relationships.