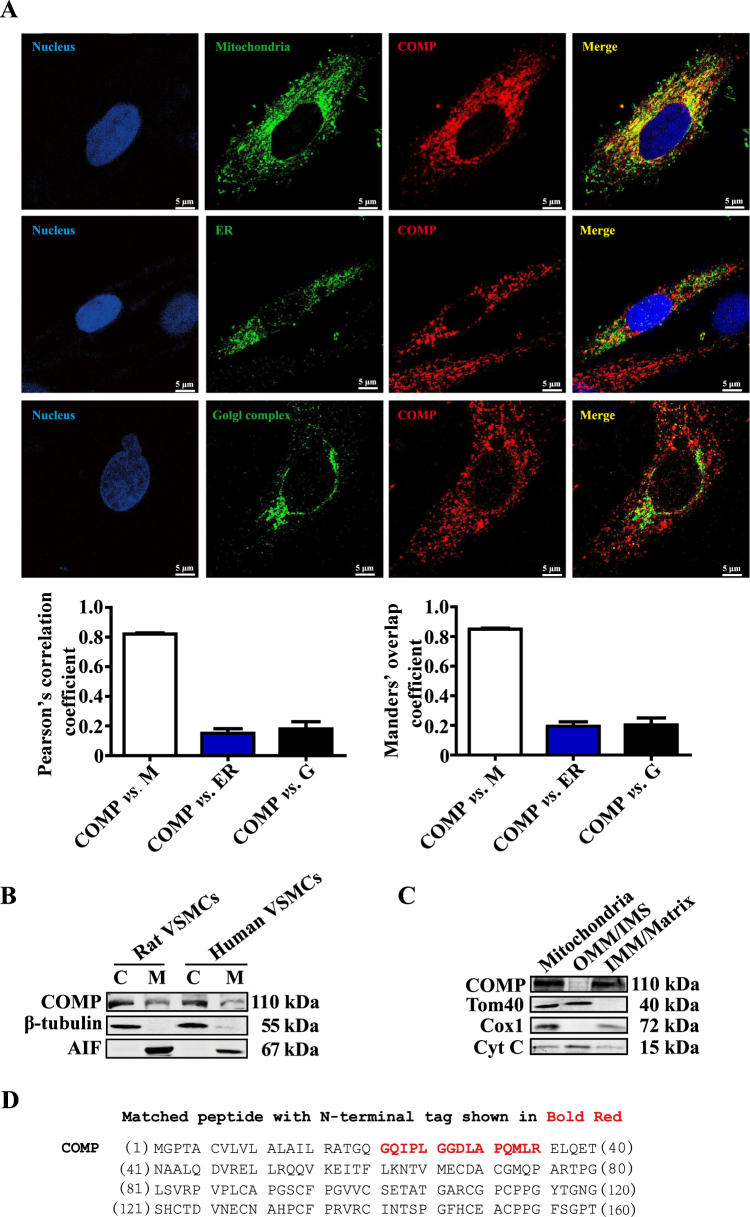
Fig. 1. COMP is intracellularly localized in mitochondria.
a Subcellular localization of COMP as demonstrated by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Mito-Tracker, TGN46 and ERp5 were used to indicate the mitochondria, Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum, respectively. Colocalization was evaluated on basis of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient and Manders’ overlap coefficient from 20–30 cells in 4 independent studies\. Scale bar = 5 μm. b Cell fractionation prior to the western blot analysis of COMP expression. Tubulin and AIF were used as cytoplasmic and mitochondrial markers, respectively. c Mitochondria isolated from rat VSMCs were subjected to subfractionation prior to the identification of COMP by western blot. Tom40 and Cox1 were used as markers for the mitochondrial outer and inner membranes, respectively. Cytochrome c is a dynamic component of mitochondria and is present in both the inner membrane and intermembrane space. d Sequence of mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial cytoplasmic COMP. The potential common N-terminus of mitochondrial COMP and non-mitochondrial cytoplasmic COMP is in bold red. e The MS/MS spectrum of the peptide (GQIPLGGDLAPQMLR) that matches the N-terminal sequence of non-mitochondrial cytoplasmic and mitochondrial COMP. M mitochondria, ER endoplasmic reticulum, G golgi complex, C cytoplasm, M mitochondria, OMM outer mitochondrial membrane, IMS intermembrane space, IMM inner mitochondrial membrane, Matrix mitochondrial matrix