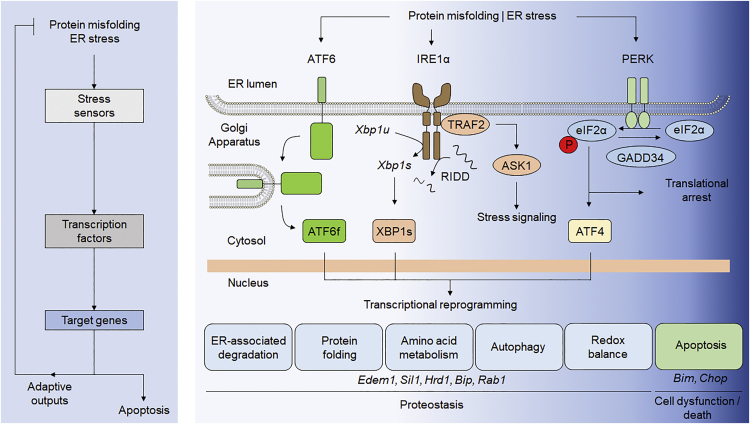
Figure 1.
ER Stress and the UPR
Left: flowchart showing the hallmarks of the UPR activation under ER stress. Right: principal components and potential targets of the UPR to modulate in disease by AAV-mediated gene therapy approaches. ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; ATF6f, fragmented activating transcription factor 6; BiP, binding immunoglobulin protein; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; EDEM1, ER degradation-enhancing alpha-mannosidase-like 1; eIF2α, eukaryotic translation initiation factor-2 alpha; GADD34, growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 34; Hrd1, hypoxia responsive domain-1; IRE1, inositol-requiring enzyme 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PERK, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; PP1, protein phosphatase 1; Rab1, Ras-associated binding protein 1; Sil1, SIL1 nucleotide exchange factor 1; TRAF2, TNF receptor-associated factor 2; Xbp1s, spliced X-box binding protein 1; Xbp1u, unspliced X-box binding protein 1.